Figure 1.
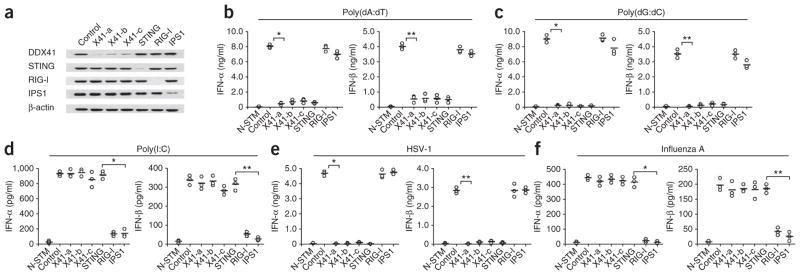
DDX41 senses cytosolic DNA in mDCs. (a) Immunoblot analysis of the knockdown efficiency of nontargeting scrambled shRNA (Control) or shRNA targeting mRNA encoding DDX41 (three shRNAs: X41-a, X41-b and X41-c), STING, RIG-I or IPS1 (above lanes) in D2SC mDCs; β-actin (bottom) serves as a loading control throughout. (b–f) ELISA of IFN-α and IFN-β in D2SC cells either treated with scrambled shRNA and left unstimulated (N-STM) or treated with scrambled shRNA (Control) or shRNA targeting mRNA encoding DDX41, STING, RIG-I or IPS1 (as in a; horizontal axis), then stimulated for 16 h with poly(dA:dT) (1 μg/ml; b), poly(dG:dC) (1 μg/ml; c), poly(I:C) (2.5 μg/ml; d), HSV-1 (multiplicity of infection (MOI), 10; e) or influenza A virus (MOI, 10; f). Each symbol represents the result of one experiment; small horizontal lines indicate the average. (b) *P < 1.5 × 10−6 and **P < 3.5 × 10−5; (c) *P < 8.3 × 10−6 and **P < 2.8 × 10−5; (d) *P < 5.2 × 10−5 and **P < 9.5 × 10−5; (e) *P < 8.10 × 10−7 and **P < 6.0 × 10−6; and (f) *P < 3.2 × 10−5 and **P < 2.0 × 10−4 (Student’s t-test). Data are from at least three independent experiments.
