Figure 4.
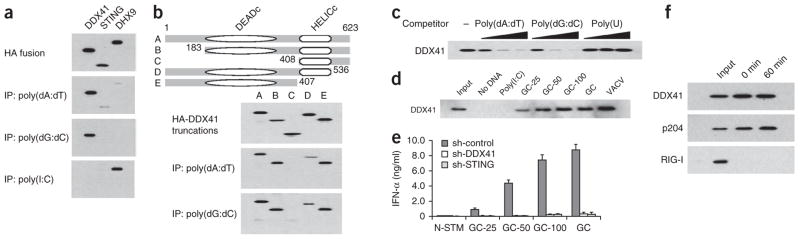
DDX41 interacts with DNA but not with RNA. (a) Immunoblot analysis of immunoprecipitation (IP) assays of purified HA-tagged DDX41, STING or DHX9 incubated with biotinylated poly(dA:dT), poly(dG:dC) or poly(I:C), probed with anti-HA. (b) Immunoblot analysis of immunoprecipitation assays of purified HA-tagged full-length DDX41 (A) and serial truncations of DDX41 (B–E) incubated individually with biotinylated DNA, probed with anti-HA. Top, full-length and serial truncations of DDX41. DEADc, Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp motif; HELICc, helicase C-terminal domain; numbers indicate positions of amino acids. (c) Immunoblot analysis of nucleic acid–immunoprecipitation competition assays of increasing concentrations of DNA or poly(U) (0.5, 5 or 50 μg/ml; wedges) or no nucleic acid (−) added to a mixture of HA-tagged DDX41 plus biotinylated poly(dA:dT), probed with anti-HA. (d) Immunoblot analysis of immunoprecipitation assays of purified HA-tagged DDX41 incubated with avidin beads alone (No DNA) or with various biotinylated RNA or DNA substrates plus avidin beads, probed with anti-HA. Input, 10% of the purified HA-tagged DDX41; GC-25, GC-50 or GC-100, poly(dG:dC) 25, 50 or 100 nucleotides in length; GC, full-length poly(dG:dC); VACV, vaccinia virus. (e) ELISA of IFN-α in D2SC cells treated with control shRNA (sh-control) or shRNA targeting DDX41 (sh-DDX41) or STING (sh-STING) and left unstimulated (N-STM) or stimulated with poly(dG:dC) of various lengths (as in d). (f) Immunoblot analysis of endogenous DDX41, p204 and RIG-I in D2SC cells incubated for 0 or 60 min with biotinylated poly(dA:dT). Input, 10% of the D2SC lysate. Data are representative of three independent experiments (mean and s.d. in e).
