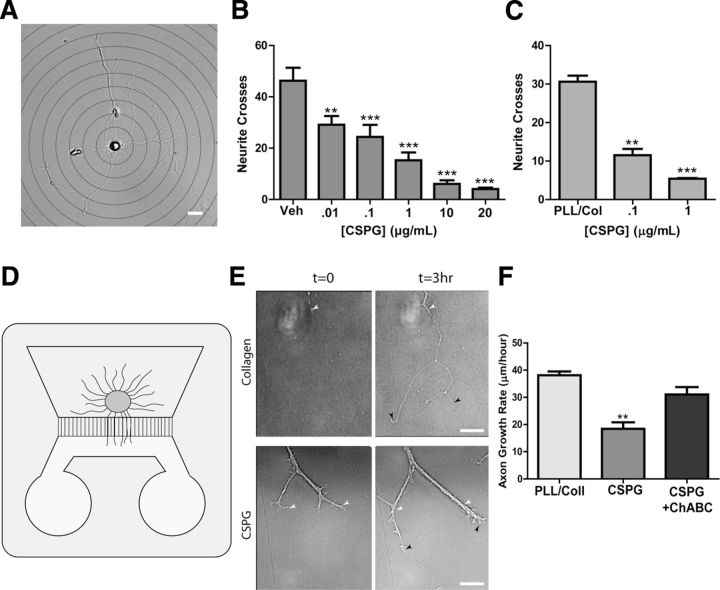
Figure 4.
CSPGs inhibit sympathetic axon outgrowth in vitro. A, A representative image of a sympathetic neuron, overlaid with a series of concentric circles for Sholl analysis. Scale bar, 20 μm. Dissociated sympathetic neurons were treated with soluble CSPGs (B), or plated onto dishes precoated with CSPGs (C), and neurite crosses were quantified by Sholl analysis. Data are the mean ± SEM of at least 10 neurons/condition, **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. D, Illustration of a microfluidic chamber with a ganglion explant on one side and axons growing through grooves into a second chamber that was coated with collagen or CSPGs. E, Representative micrographs of axons growing at t = 0 and t = 3 h on collagen or CSPGs (1 μg/ml). White arrowheads indicate the leading edge of the axon in the t = 0 image, while black arrowheads indicate the final point of the axon at t = 3 h. Scale bar, 20 μm. Note bundling of the axons growing on CSPGs. F, Quantification of axon growth in microfluidic chambers where the distal compartment was coated with collagen, collagen/CSPGs, or collagen/CSPGs + ChABC. Data are mean ± SEM for at least eight axons per condition, **p < 0.01, and similar results were obtained in three independent experiments.