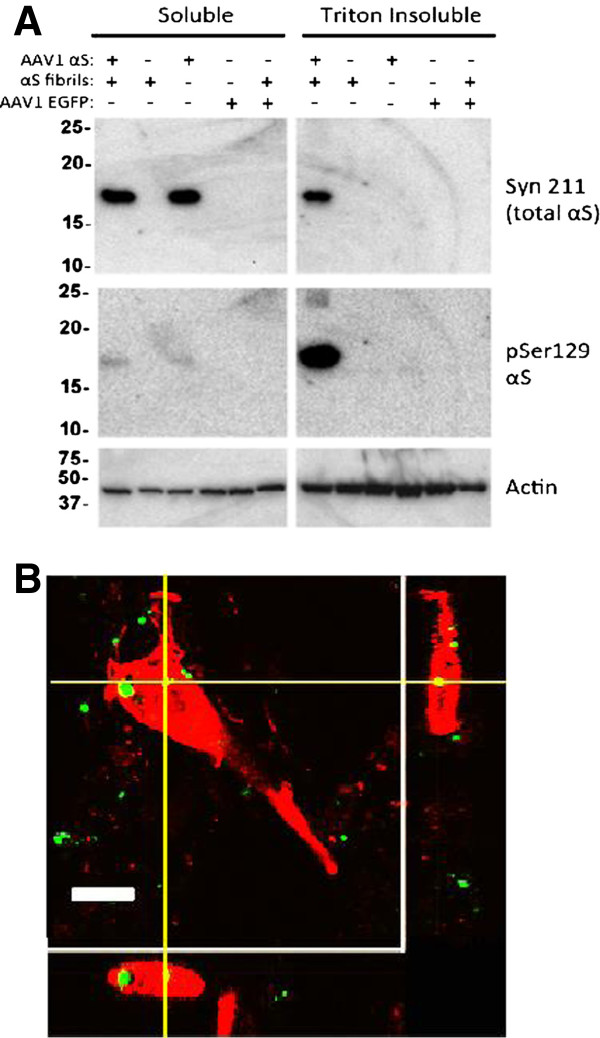
Figure 3.
Extracellular αS fibril uptake by cells and formation of intracellular Triton-insoluble αS aggregates. (A) Formation of intracellular Triton-insoluble αS aggregates induced by extracellular αS amyloid fibrils. Cultures were treated with either rAAV2/1 wild-type αS or rAAV2/1 EGFP (green fluorescent protein control) alone or in combination with wild-type αS fibrils. Four days post-seeding, cultures were biochemically fractionated using Triton X-100 containing buffer as described in Materials and Methods. Aggregated αS is found in the Triton-insoluble fraction. Syn211, which recognizes the overexpressed human αS, showed bands in the soluble fractions treated with rAAV2/1 wild-type αS. Only with both the rAAV2/1-mediated overexpression of human αS plus the addition of extracellular αS fibrils is αS present in the Triton-insoluble fraction. pSer129, which recognizes the hyperphosphorylated aggregates, also showed a band for αS with both the overexpression of αS plus αS fibrils in the Triton-insoluble fraction. (B) Z-slice section analysis of αS inclusions showing incorporation of extracellular fibrils into aggregates. Thioflavin-S pre-labeled wild-type αS fibrils (green) are incorporated into pSer129 aggregates (red). Bar scale = 10 μm.