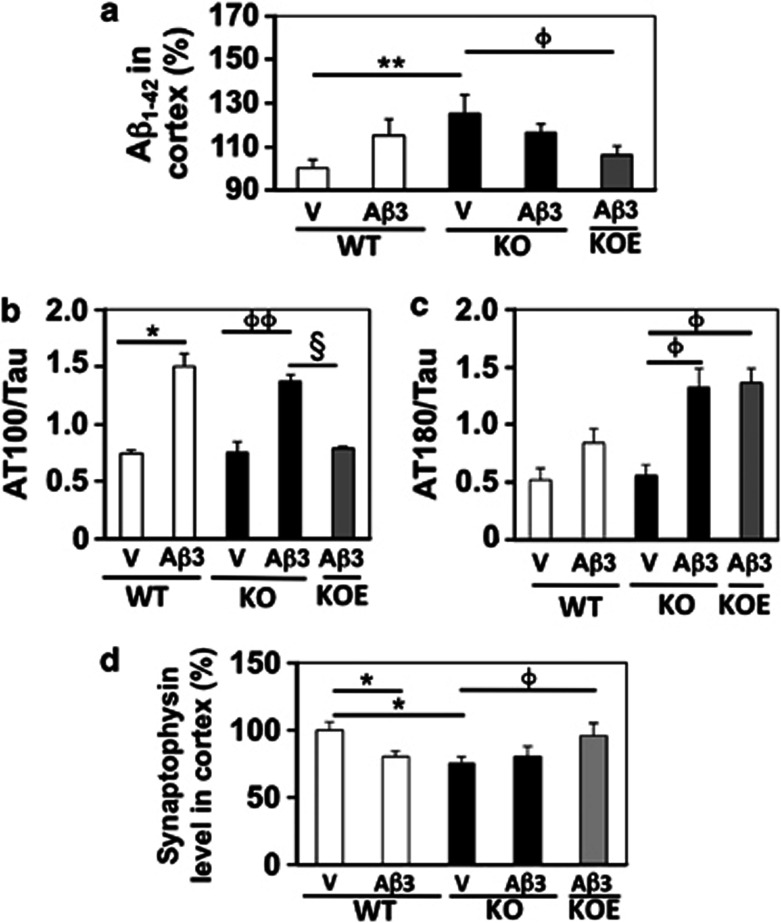
Figure 4.
(a) APP processing, (b, c) Tau phosphorylation and (d) synaptophysin levels in Aβ25–35-injected PLTP-KO mice. WT and PLTP-KO mice, supplemented in vitamin E (KOE) or not (KO), received an i.c.v. injection of sterile water (V) or Aβ25–35, 3 nmol (Aβ3). They were killed after 7 days. (a) Aβ1–42 content was quantified in cortex homogenates by ELISA. ANOVA: F(4,95)=4.03, P<0.01, n=14–23. (b, c) Tau phosphorylation was measured by western blots using AT100 and AT180 monoclonal antibodies and normalized to total Tau protein. (d) Synaptophysin was quantified in cortex homogenates by ELISA. ANOVA: F(4,92)=2.77, P<0.05, n=13–23 in (b); F(4,67)=2.71, P<0.05, n=13–17 in (c); F(4,68)=2.66, P<0.05, n=12–17 in (d). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs V-treated WT group; φP<0.05, φφP<0.01 vs V-treated PLTP-KO group; §P<0.01 vs Aβ3-treated PLTP-KO group; Bonferroni's test.