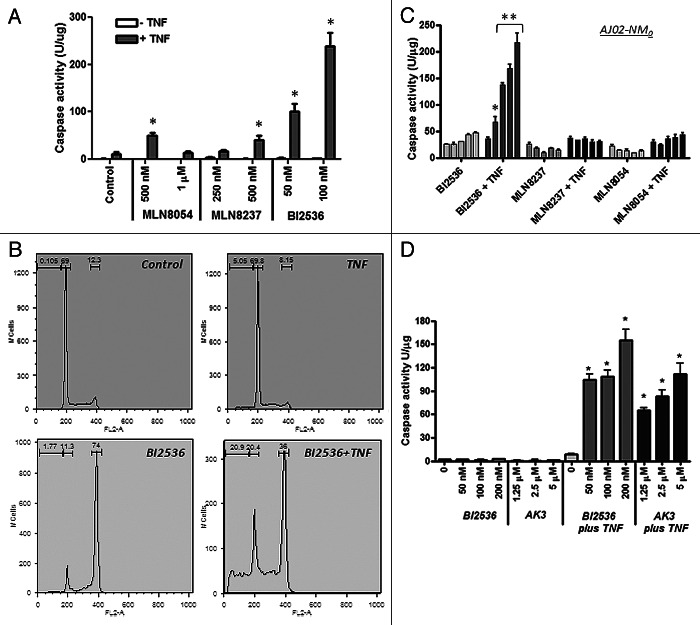
Figure 9. Effect of kinase inhibitors on the TNF sensitivity of colon cancer cells. (A) TNFinduced caspase activation in the presence of MLN8054, MLN8237 (Aurora A kinase inhibitors) and BI2536 (Plk1 inhibitor). HT29 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of the inhibitors in the presence or absence of TNF and tested for caspase-3 activity using the DEVD-AMC substrate. BI2536 induced a significantly higher level of caspase activation than the Aurora kinase inhibitors (ANOVA, p < 0.01). (B) Cell cycle analysis of HT29 cells treated with BI2536 in the presence or absence of TNF. BI2536 at 100 nM induces a G2/M arrest and, in combination with TNF, causes the appearance of sub-diploid cells. (C) BI2536 enhances TNF-induced apoptosis in the mouse AJ02-NM0 colon cancer cell line more potently than MLN8054 or MLN8237. AJ02-NM0 cells were treated with the inhibitors in the presence or absence of murine TNF and tested for caspase activation using the DEVD-AMC substrate. Inhibitors were used at 0, 125, 250, 500 and 1000 nM (from left to right). BI2536 was a significantly more potent sensitizing agent than the Aurora kinase inhibitors at all concentrations tested (ANOVA; *p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01). (D) AK3 and BI2536 induce comparable levels of caspase activation in HT29 cells in the presence of TNF. Cells were treated with the indicated agents and tested for caspase activation using the DEVD-AMC substrate. AK3 and BI2536 in combination with TNF induced significantly higher caspase activity than either individual treatment (ANOVA; *p < 0.01).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.