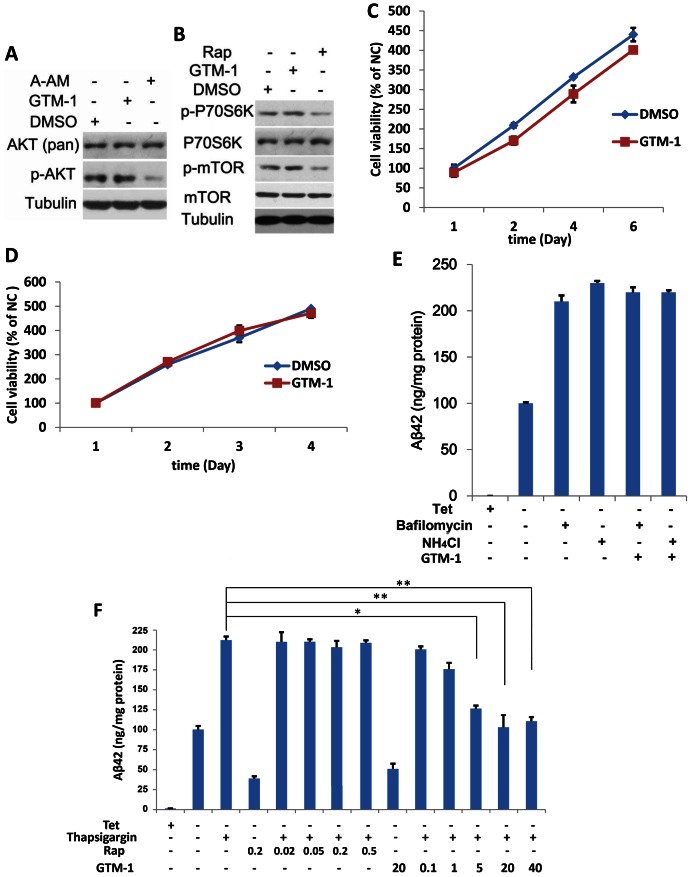
Figure 4. GTM-1 modulates autophagy in neurons using a different mechanism from rapamycin.
A–B, SH-SY5Y cells were treated with the indicated compounds for 12 hrs. Next, the cell lysates were analyzed using western blotting with specific antibodies. DMSO (0.1%), GTM-1 (20 µM), Rap: Rapamycin (0.2 µM), A-AM (0.1 µM). β-tubulin was used a control. C–D, SH-SY5Y (4C) or MC-65 (4D) cells were incubated with GTM-1 (20 µM) for the indicated times. Cells treated with vehicle (0.1% DMSO) for 24 hrs were used as a negative control (NC). Cell viability was assessed using MTT, and all of the data were normalized to the NC. E, MC65 cells were grown in the presence (Tet+) or absence (Tet−) of tetracycline and under Tet− with GTM-1 (20 µM) for 8 hrs. The indicated compounds were then added within 2 hrs. Soluble Aβ oligomers were assessed using ELISA in MC65 cells. Bafilomycin (100 nM), NH4Cl (10 mM). F, MC65 cells were grown in the presence (Tet+) or absence (Tet−) of tetracycline and under Tet− with GTM-1 (at indicated concentrations) for 5 hrs, and the indicated compounds were added within 5 hrs. The soluble Aβ oligomers were assessed using ELISA. Rap: Rapamycin (at the indicated concentrations), thapsigargin (3 µM). Stars indicate significant differences between the model group and control or treatment groups for specific time points. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.