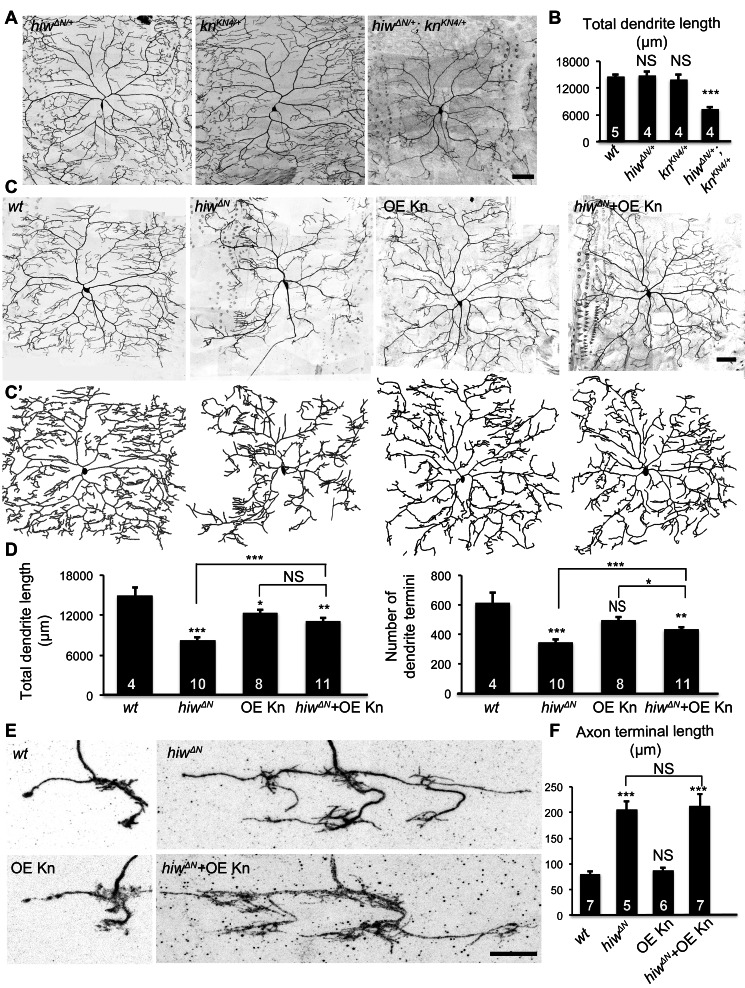
Figure 5. Kn specifically mediates Hiw regulation of dendritic growth.
(A) hiw and kn interact genetically. Shown are representative dendrites of the following genotypes: (1) hiwΔN heterozygote (hiwΔN/+); (2) kn KN4 heterozygote (knKN4/+); (3) hiwΔN and knKN4 trans-heterozygote (hiwΔN/+; knKN4/+). Scale bar, 50 µm. (B) Quantification of total dendrite length of denoted genotypes. wt samples used for statistical analysis are the same as those in Figure 1. (C and C′) Overexpressing Kn partially rescues dendritic defects in hiwΔN mutants. Representative dendrites (C) and tracings (C′) of ddaC MARCM clones of following genotypes: (1) wt; (2) hiwΔN; (3) overexpressing Kn with MARCM (OE Kn); (4) overexpressing Knot in hiwΔN genetic background with MARCM (hiwΔN+OE Kn). Scale bar, 50 µm. (D) Quantification of total dendrite length (left) and number of dendrite termini (right). (E) Overexpressing Kn does not alter axon terminal morphology in hiwΔN mutants. Shown are representative axon terminals of ddaC MARCM clones of the indicated genotypes. Scale bar, 10 µm. (F) Quantification of the length of axon terminals.