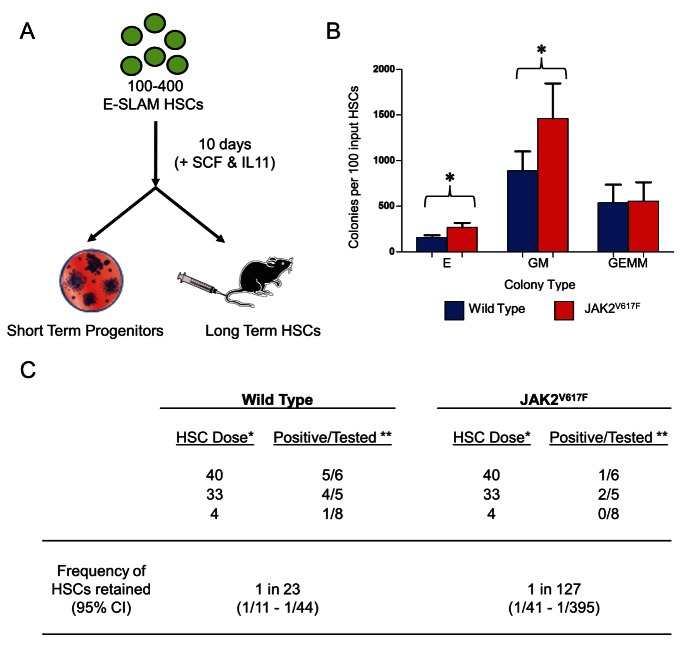
Figure 3. Cultured JAK2V617F E-SLAM HSCs produce more short-term progenitors, but lack long-term reconstitution ability.
(A) Cells derived from cultures of 100–400 E-SLAM HSCs were harvested after 10 d of culture in SCF and IL-11 and then placed in a colony-forming cell (CFC) assay to determine the number and type of progenitor cells made or were transplanted into irradiated recipients to determine whether or not long-term reconstituting ability was retained. (B) Following 10–14 d of culture in the CFC assay, colonies were scored and enumerated. Colonies were scored as either Erythroid (E), Granulocyte/Macrophage (GM), or Granulocyte/Macrophage/Erythroid/Megakaryocyte (GEMM) progenitors and are represented by bar graphs showing the mean +/– SEM of four to six biological replicates from four independent experiments. A greater number of GM (p = 0.009) and E (p = 0.007) were observed in CFCs derived from JAK2V617F cultures. (C) Varying doses (40, 33, 4) of HSC starting equivalents (the proportion of the total culture that would have been made by that input number of HSCs) were transplanted to determine the frequency of cells that had retained long-term reconstituting ability in two independent experiments. This is followed by a limiting dilution analysis that estimates the frequency of HSCs retained in the culture. Cultures of JAK2V617F HSCs make 5–6-fold fewer HSCs in culture compared to WT littermate controls (p = 0.00469). * HSC dose is defined as the number of starting equivalents that were transplanted. In the case of “40,” this is representative of transplanting all of the cells that would be generated from a 10-d culture of 40 HSCs. ** A mouse was considered to be positive if it had >1% donor chimerism at 16–24 weeks and represented at least 0.5% of each lineage (GM, B, and T) at some point over the 16-wk period.