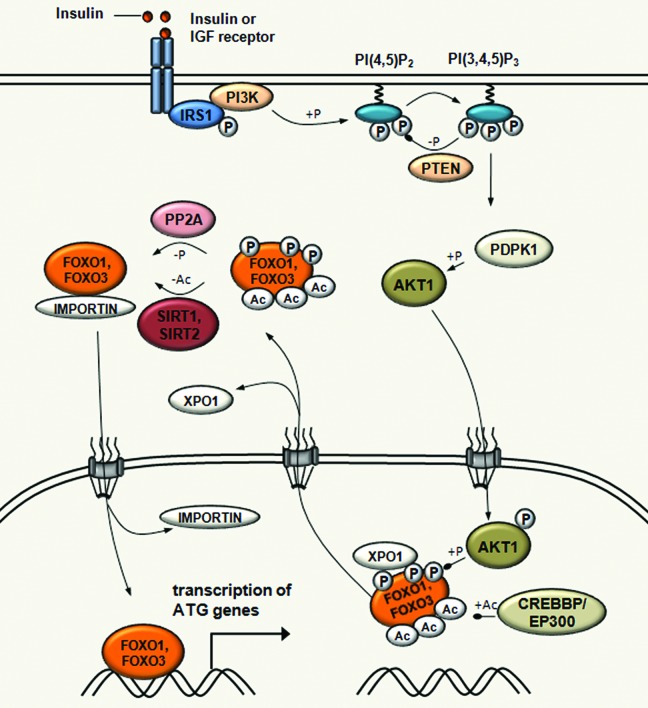
Figure 3. Acetylation-mediated control of FOXO transcription factor activity in autophagy regulation. SIRT1 induces autophagy through the deacetylation of FOXO1 upon starvation. SIRT1 also deacetylates FOXO3, which is required for the transcriptional activation of genes that are involved in autophagosome formation, such as MAP1LC3, PIK3C3, GABARAPL1, ATG12, ATG4, BECN1, ULK1 and BNIP3. In fed conditions, EP300-CREBBP acetyltransferases increase FOXO1 and FOXO3 acetylation, which results in decreasing their DNA binding activity and in increasing their sensitivity to phosphorylation. In response to insulin, FOXO1 and FOXO3 are phosphorylated by AKT1 leading to its dissociation from DNA and subsequent export to the cytoplasm through XPO1/CRM1-mediated export.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.