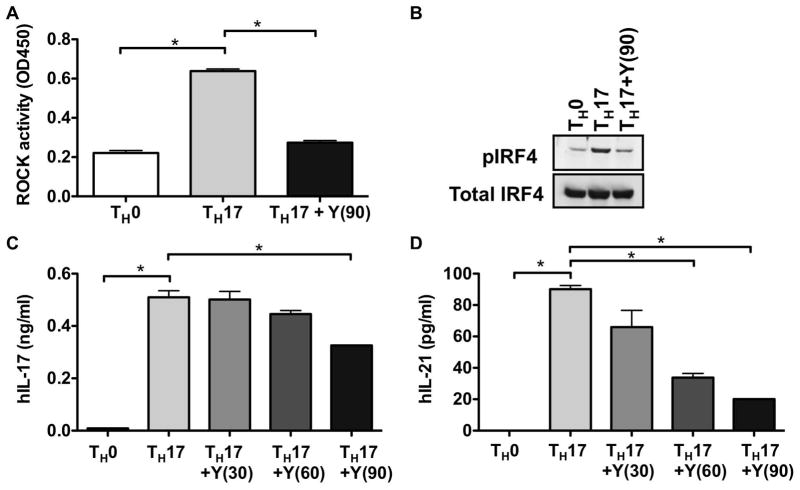
Figure 2. ROCK activation in human TH-17 cells.
(A) Human CD4+ T cells from cord blood (106 cells/well) were stimulated under either TH0 or TH17 skewing conditions in the presence or absence of Y-27632 (90μM). ROCK activation was assessed at day 3 by an ELISA-based ROCK kinase activity assay. (B) Human CD4+ T cells from cord blood were stimulated as in (A) in the presence or absence of Y-27632 (90μM) and extracts were analyzed by Western blotting using an antibody that recognizes phosphorylated IRF4 (pIRF4) (upper panel). The blot was later stripped and reprobed with an antibody against total IRF4 (lower panel). Human CD4+ T cells from cord blood were stimulated as in (A) in the presence or absence of Y-27632 (30–90μM as indicated) and the levels of (C) IL-17 and (D) IL-21 in the supernatants were assessed by ELISA. Shown is one representative experiment of three independent experiments. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post test analysis; *p<0.05. Y(30): 30μM Y-27632; Y(60): 60μM Y-27632; Y(90): 90μM Y-27632.