Figure 3. Alcohol intoxication disrupts neuroendocrine compensatory mechanisms in response to blood loss.
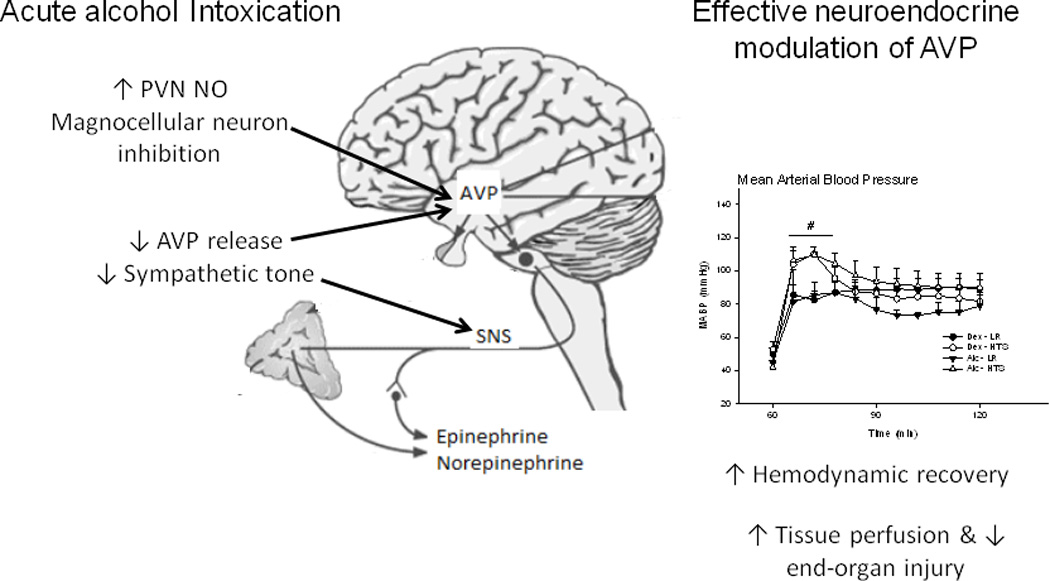
AAI upregulates PVN NO expression exerting an inhibitory tone on AVP release and attenuation of epinephrine, norepinephrine, and angiotensin II release in response to blood loss. Increased resuscitation fluid osmolarity sensitizes the AVP response to blood loss, improves hemodynamic recovery in the AAI host, This modulation of neuroendocrine response was associated with marked improvement in restoration of blood pressure, improved tissue perfusion, and attenuated end organ injury reflected in decreased gut leak. AAI, acute alcohol intoxication; AVP, arginine vasopressin; NO, nitric oxide, PVN, periventricular nucleus.
