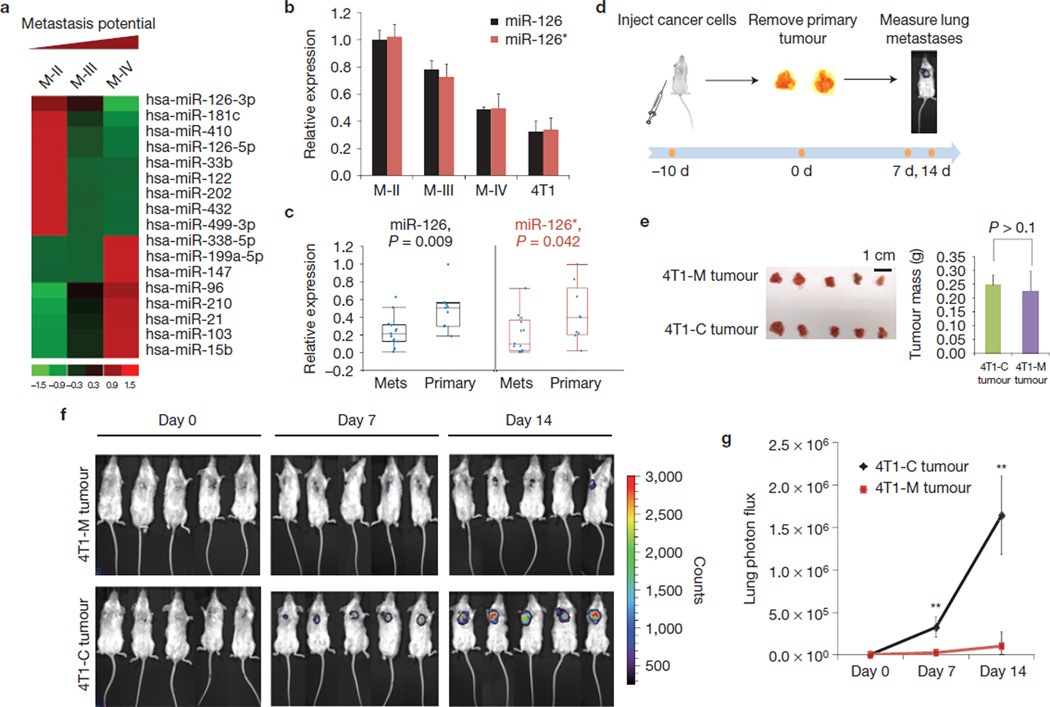
Figure 1.
Identification of miR-126 and miR-126* as potential suppressors of breast cancer metastasis. (a) A partial list of microRNAs whose expression pattern correlates with metastatic potential in M-II (MCF10 AT1k, benign), M-III (MCF10 Ca1h, low metastatic) and M-IV (MCF10 Ca1a.c11, high metastatic) cells. A total of 242 microRNAs were tested in a quantitative-rtPCR-based array as previously described20. Data were normalized using U6 RNA. (b) miR-126 and miR-126* expression were inversely correlated with metastatic potential. The relative expression levels of miR-126 and miR-126* were measured by quantitative rtPCR and normalized to U6 RNA. The data presented are shown as mean±s.d. collected from three independent experiments. (c) miR-126 and miR-126* are expressed at a higher level in primary breast tumours than in metastatic tumour samples. The relative expression levels of miR-126 and miR-126* in 9 primary and 13 metastatic tissues were measured by quantitative rtPCR and normalized to U6 RNA. In the box-and-whisker plot, each point represents one sample. The central box represents the values from the lower to upper quartile. The middle line represents the median. The horizontal line extends from the minimum to the maximum value excluding far-out values. (d) Schematic procedure of in vivo tumour implantation and lung metastases measurement. (e) Pri-miR-126 ectopic expression had little impact on primary tumour size or weight. Approximately 5×104 control or ectopic pri-miR-126-expressing 4T1 cells harbouring a luciferase reporter were implanted into the mammary fat pad of 6-week-old female BALB/c mice. After 10 days, tumours grown at the primary site were surgically removed and weighed. The data presented are shown as mean±s.d. collected from five independent experiments. (f) Pri-miR-126 suppressed the formation of lung metastases by 4T1 cells. Metastatic lung lesion formation was monitored by the appearance of luciferase activity using imaging apparatus 7 and 14 days after primary tumour removal, n = 5 in each group. (g) Quantification of the results shown in f. The data are shown as mean±s.d. collected from five independent experiments. **P < 0.01.