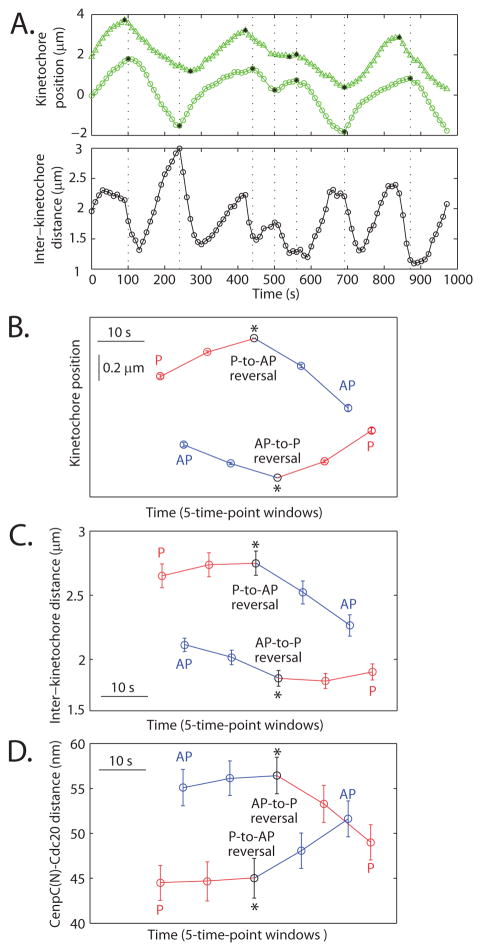
Fig. 2.
Distance between sister kinetochores and between probes in one kinetochore during direction reversals. (A) Single kinetochore position (top) and inter-kinetochore distance (bottom) over time for a sister kinetochore pair (the one in Fig. 1C). Black stars = direction reversals. (B) Mean kinetochore position, (C) inter-kinetochore distance and (D) CenpC(N)-Cdc20 distance over time for metaphase P-to-AP (n=104 traces) and AP-to-P (n=98 traces) reversals (P in red, AP in blue). AP-to-P reversals are positioned 6 s later than P-to-AP on the time axis to reflect the average time between them. Bars = s.e.m. Direction reversals cause abrupt changes in inter-probe distance with a kinetochore, consistent with a mechanical response to a change in force.