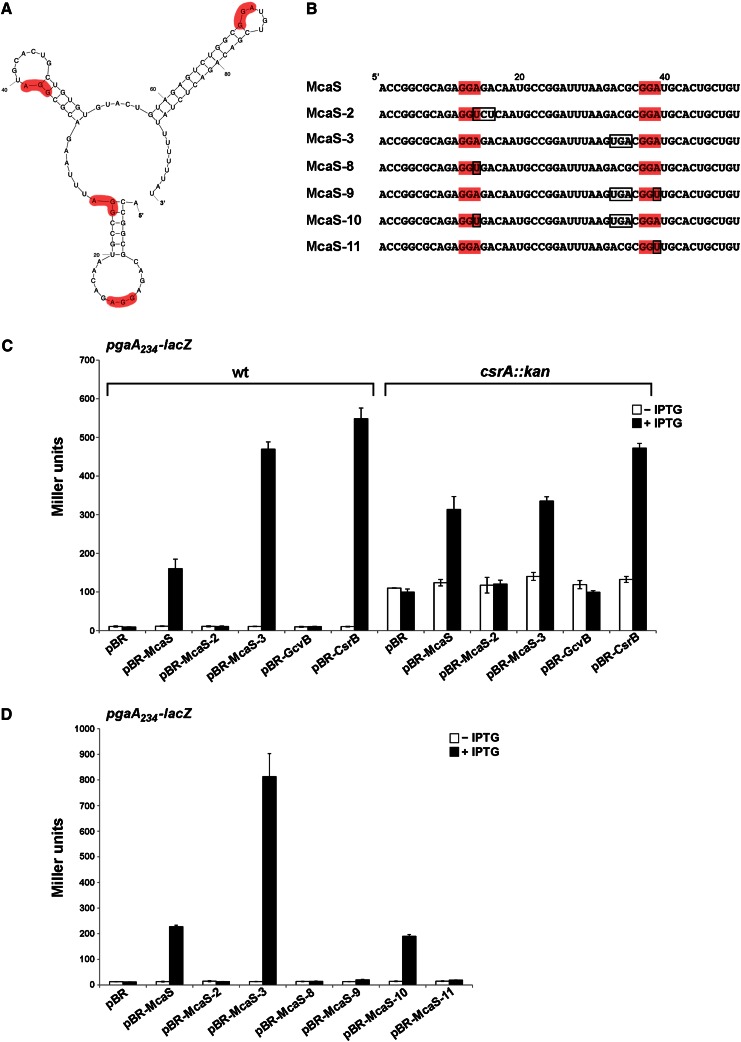
Figure 2.
CsrA dependence of McaS-mediated effects on pgaA-lacZ expression. (A) Predicted structure of wild-type McaS showing putative CsrA-binding sites (highlighted in red). (B) The sequences of the first 50 nt of wild-type McaS and mutant derivatives. Nucleotides altered for each mutant are boxed. Putative CsrA-binding sites are shaded in red. (C) McaS-dependent activation of pgaA-lacZ expression requires functional CsrA. The reporter stains PM1205 ΔabgR-ydaL ΔpgaA∷cat pgaA234-lacZ and PM1205 ΔabgR-ydaL ΔpgaA∷cat csrA∷kan pgaA234-lacZ were transformed with the control vector, pBR-McaS, pBR-McaS-2, pBR-McaS-3, pBR-GcvB, and pBR-CsrB. (D) McaS mutants carrying disrupted GGA motifs do not activate pgaA-lacZ expression. The reporter strain PM1205 ΔabgR-ydaL pgaA234- lacZ was transformed with the control vector, pBR-McaS, and plasmids expressing McaS mutant derivatives. β-Galactosidase activity in C and D was assayed as in Figure 1.