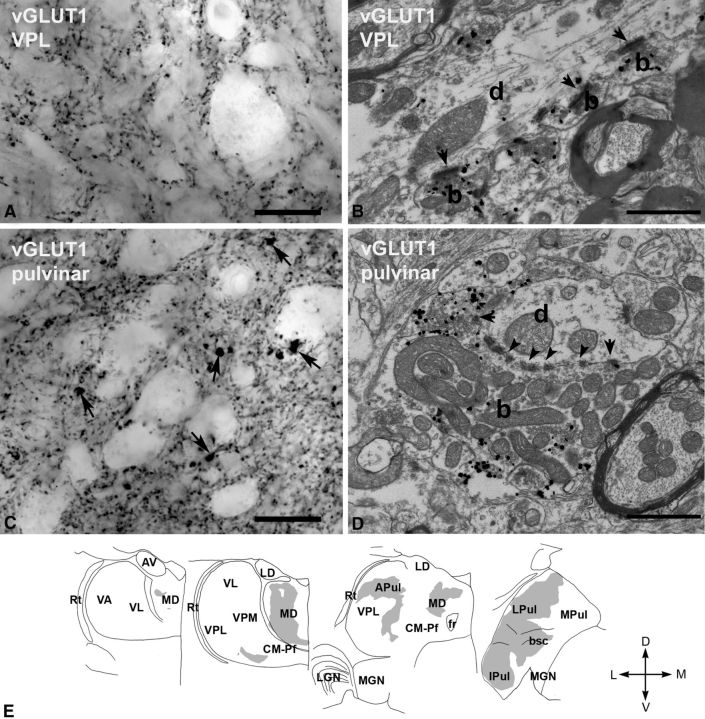
Figure 3.
vGLUT1-immunoreactive terminals in the macaque thalamus. A, High-power light microscopic image of a vGLUT1-immunostained section from the VPL displaying small vGLUT1-immunoreactive terminals only. B, At the electron microscopic level, these terminals (b, silver-intensified gold) display the features of RS-type terminals, i.e., small size, maximum of one or two mitochodria, no puctum adherens, and a single synapse (arrow). d, Postsynaptic dendrite. C, In the lateral pulvinar, besides the small vGLUT1-immunoreactive terminals, large immunoreactive structures (arrows) can also be distinguished at the light microscopic level. D, At the electron microscopic level, a large vGLUT1-immunoreactive terminal (b, silver-intensified gold) displays all the ultrastructural features of RL terminals. Arrows, Synapses; arrowheads, puncta adherentia; d, postsynaptic dendrite. E, Regional distribution of large vGLUT1-positive terminals at four coronal levels of the macaque thalamus. Note the lack of large vGLUT1-positve terminals from many thalamic nuclei considered as higher order and the heterogeneity of the distribution within the mediodorsal nucleus (MD) and pulvinar. Scale bars: A, C, 20 μm; B, D, 1 μm. APul, Anterior pulvinar; AV, anteroventral; bsc, brachium of superior colliculus; CM–Pf, centromedian–parafascicular; fr, fasciculus retroflexus; Ipul, inferior pulvinar; LD, laterodorsal; LGN, lateral geniculate nucleus; LPul, lateral pulvinar; MD, mediodorsal; MGN, medial geniculate nucleus; MPul, medial pulvinar; VA, ventral anterior; VL, ventrolateral; VPL, ventral posterolateral; VPM, ventral posteromedial; Rt, reticular thalamus.