Figure 5.
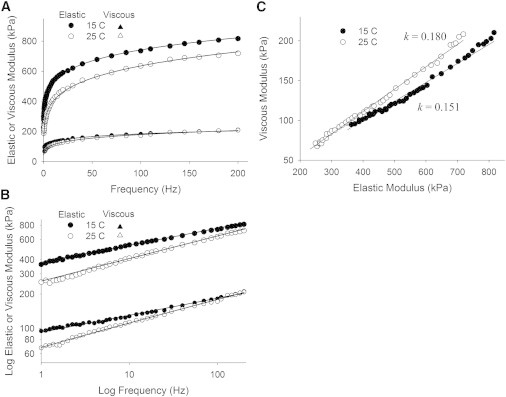
Recorded elastic and viscous moduli from human MHC I skeletal muscle at different temperatures. (A) An increase in temperature from 15°C to 25°C did not result in a statistically significant change in E. (B) The log-log plot of each moduli pair again demonstrates parallel lines for each condition. (C) The 10°C rise in temperature resulted in a ∼19% rise in parameter k and a corresponding reduction in the average crosslink lifetime. A Q10 of 1.19 is within the range of expected sensitivities to temperature for nonenzymatic processes.
