Figure 6.
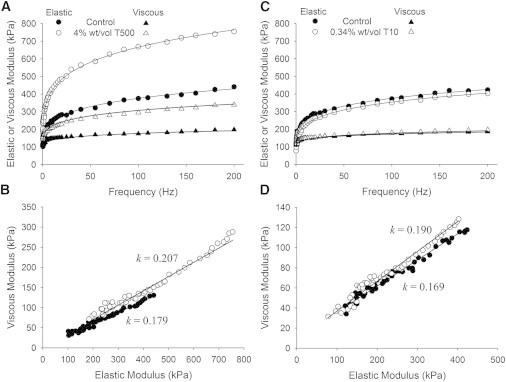
Recorded elastic and viscous moduli from human MHC I skeletal muscle at 4% w/v Dextran T500 and 0.34% w/v DextranT10, which are osmolytes. (A and B) With the application of 4% w/v Dextran T500, the myofilament lattice was compressed and distances between thick and thin filaments were shortened. The magnitudes of the elastic and viscous moduli were significantly increased with the compressed lattice spacing, which we attribute to the enhanced probability of crosslink formation due to the closer proximity of thick and thin filaments. (C and D) The application of 0.34% w/v Dextran T10 caused dehydration of protein structures similar to that of 4% w/v of T500 without changing myofilament lattice spacing and resulted in a rise in parameter k, which corresponded to a reduction in mean crosslink lifetime due to dehydration.
