Figure 2.
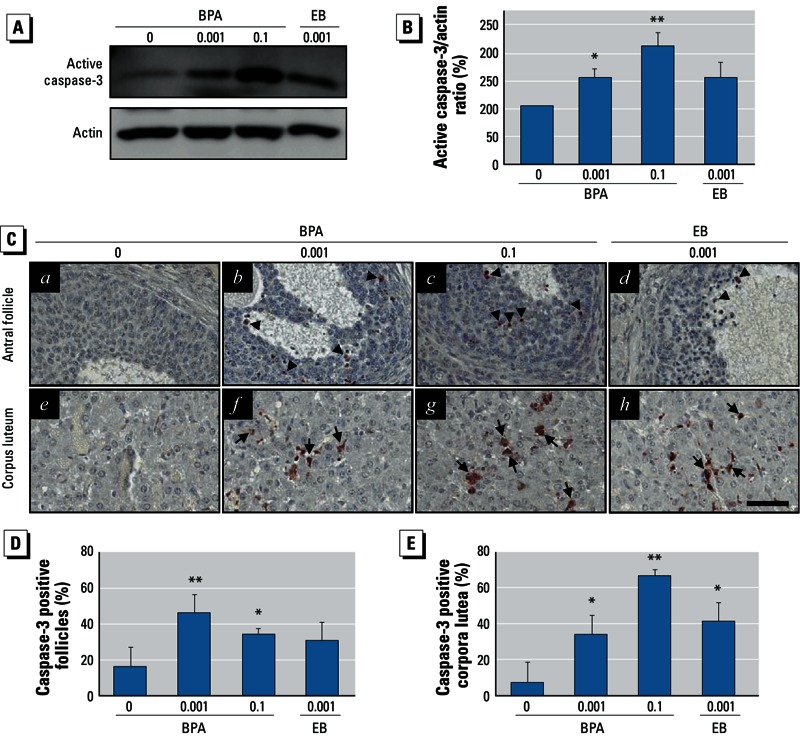
Effect of BPA on caspase-3–associated apoptotic cell death in ovarian cells and follicular atresia augmentation and luteal regression. Adult female rats were administered BPA (0, 0.001, or 0.1 mg/kg BWU/day) or EB (0.001 mg/kg BW/day) for 90 days by gavage. (A) Caspase-3-associated apoptotic cell death in the ovaries evaluated by Western blot analysis using an active form-specific caspase-3 antibody. (B) Densitometric quantification of activated caspase-3 protein levels in total ovarian protein extracts. For (A) and (B), data represent the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. (C) Immunolocalization of active caspase-3 in ovaries. Arrowheads indicate active caspase-3-positive granulosa cells, and arrows point to luteal cells. Original magnification: 200×; bar = 60 μm. Changes in the proportion of atretic follicles (D) and the regressing corpus luteum (E) in the ovary. For B, D, and E, data represent the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, and **p < 0.01 compared with control (0 mg/kg BW).
