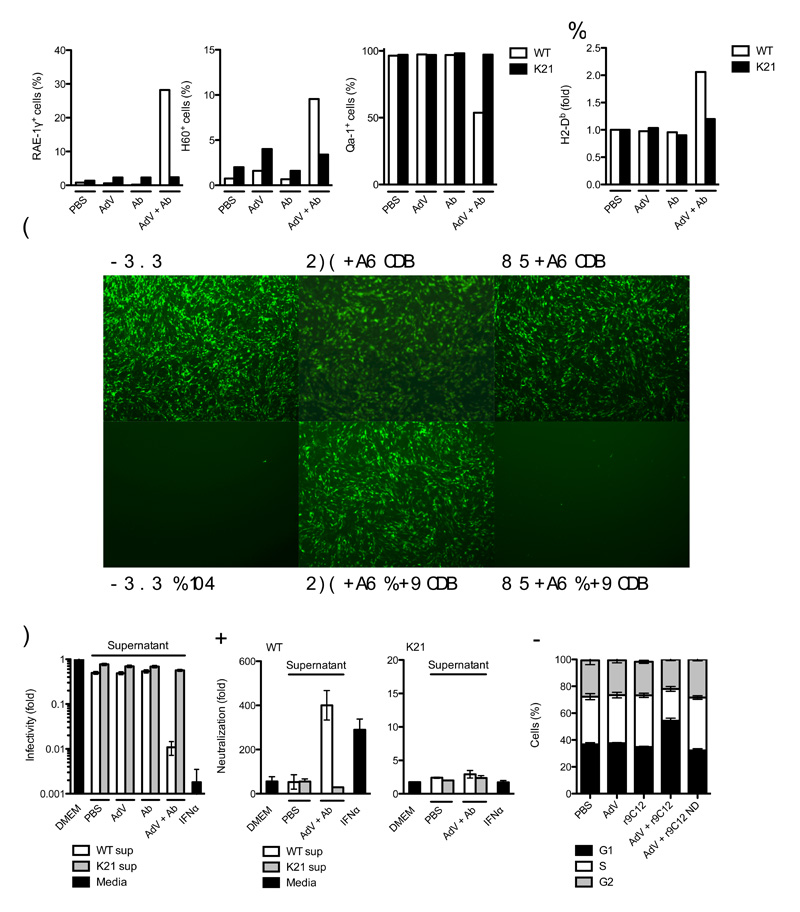
Figure 5. Detection of intracellular antibody-bound pathogens promotes an antiviral state.
(a) Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) data showing percent of wild-type (WT) or Trim21-deficient (K21) MEF cells positive for surface expression of NKG2D ligands RAE-1γ and H60 and NKG2A ligand Qa-1. (b) FACS data showing change in fluorescence intensity after staining for surface MHC class Ia allele H2-Db expression over PBS-treated control in wild-type and Trim21-deficient MEFs. (c, d) Sindbis GFP virus infection of wild-type MEF ‘reporter’ cells which were incubated with fresh media (DMEM), media supplemented with mouse IFNα or supernatant (sup) derived from wild-type or Trim21-deficient MEFs challenged with AdV, Ab or AdV + Ab. (c) Fluorescence microscope images showing wild-type MEF reporter cell monolayers 12 h after Sindbis GFP infection. (d) Percent GFP positive wild-type reporter MEF cells relative to DMEM-treated control. (E) Fold neutralization of adenovirus by monoclonal antibody 9C12 relative to PBS-treated adenovirus after treatment of wild-type and Trim21-deficient reporter cells with Fresh media (DMEM), media supplemented with IFNα or supernatant transferred from wild-type or Trim21-deficient MEFs that were either PBS-treated or challenged with AdV + Ab. (f) Propidium iodide staining showing proportion of cells in G1, S or G2 24 h after challenge with AdV or AdV complexed with recombinant 9C12 (r9C12) or 9C12 bearing a point mutation N434D (r9C12 ND). For panels a, b, d-f, error bars represent SEM from three replicates.