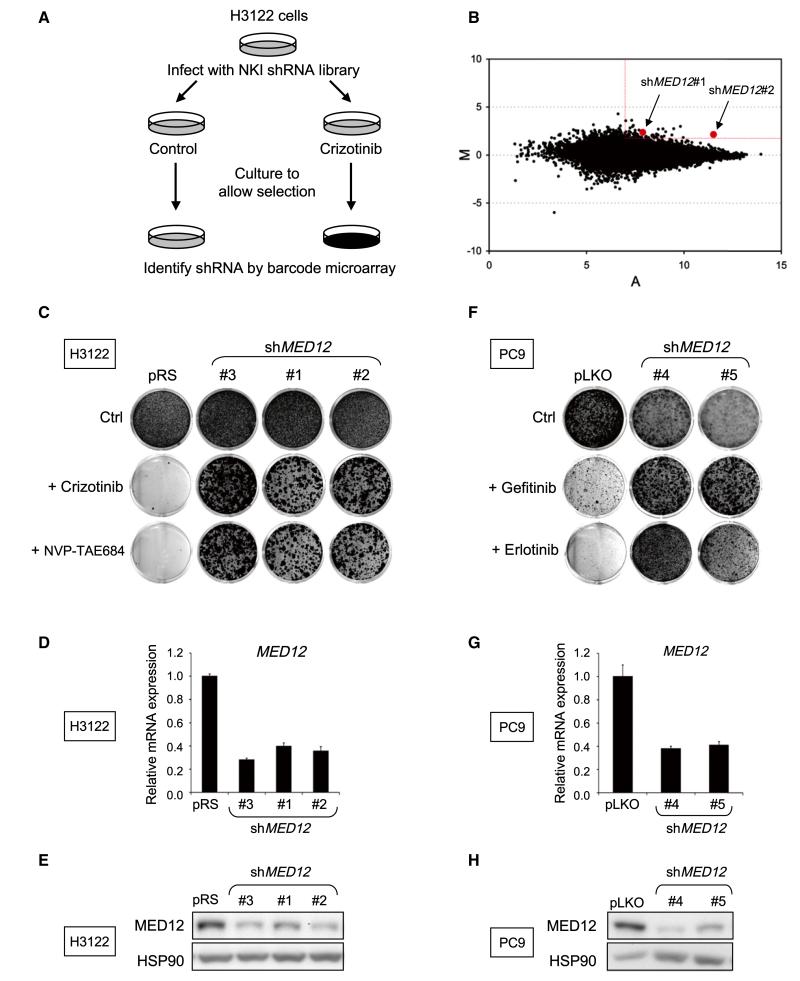
Figure 1. A Genome-wide RNAi Screen Identifies MED12 as a Critical Determinant of Drug Response to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in NSCLCs.
(A) Schematic outline of the crizotinib resistance barcode screen performed in H3122 cells. NKI human shRNA library polyclonal virus was used to infect H3122 cells, which were then left untreated (control) or treated with 300 nM crizotinib for 14 or 28 days, respectively. After selection, shRNA inserts from both populations were recovered, labeled, and hybridized to DNA oligonucleotide barcode arrays.
(B) Analysis of the relative abundance of the recovered shRNA cassettes from crizotinib barcode experiment. Averaged data from three independent experiments were normalized and 2log transformed. Among the 43 top shRNA candidates (M > 2 and A > 7), two independent shMED12 vectors (in red) were identified.
(C-E) Three independent shRNAs targeting MED12 confer resistance to ALK inhibitors. (C) The functional phenotypes of nonoverlapping retroviral shMED12 vectors (#1–3) in H3122 cells are indicated by colony formation assay in 300 nM crizotinib or 2.5 nM NVP-TAE684. The pRS vector was used as a control. The cells were fixed, stained, and photographed after 14 (untreated) or 28 days (treated). (D) The level of MED12KD by each of the shRNAs was measured by examining the MED12 mRNA levels by qRT-PCR. Error bars denote standard deviation (SD). (E) The level of knockdown of MED12 protein was measured by western blotting. (F–H) Suppression of MED12 also confers to EGFR inhibitors. (F) Colony formation assay of PC9 cells that express pLKO control or independent lentiviral shMED12 vectors (#4 and #5) and that were cultured in 50 nM gefitinib or erlotinib. The cells were fixed, stained, and photographed after 10 (untreated) or 28 days (treated). (G) The level of MED12KD by each of the shRNAs was measured by examining the MED12 mRNA levels by qRT-PCR. Error bars denote SD. (H) The level of knockdown of MED12 protein was measured by western blotting.
See also Figures S1 and S2.