Figure 5. Inflating CD8+ T cells show progressive differentiation towards polyfunctionality and maintain cytotoxicity.
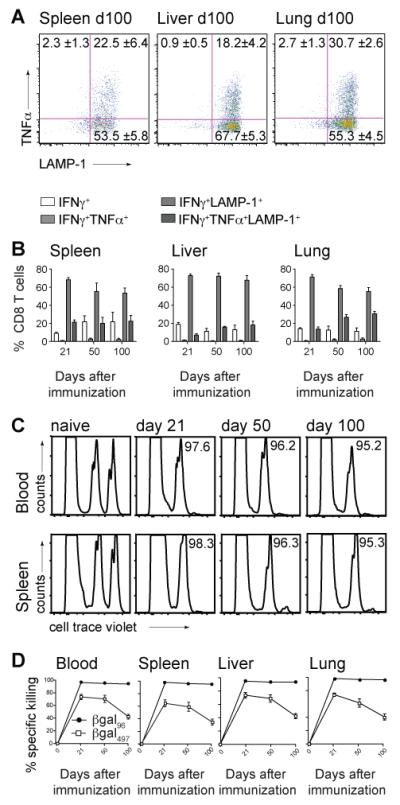
B6 mice were immunized with 2×109 pfu Ad-LacZ i.v.. (A) FACS plots show TNFα and LAMP-1 expression on day 100 in spleen, liver and lung after in vitro stimulation with the βgal96 peptide, gated on live IFNγ+ CD3+CD8+ T lymphocytes. (B) Shows IFNγ single+CD8+ T cells (white bar), IFNγ+TNFα+CD8+ T cells (light grey bars), IFNγ+LAMP1+CD8+ T cells (grey bars) and IFNγ+TNFα+LAMP-1+CD8+ T cells (dark grey bars)within the IFNγ+CD8+ T cell compartment after stimulation with the βgal96 peptide in spleen, liver and lung. Mean percentages are indicated (±SEM; spleen d21 n=6, d50 n=6, d100 n=5; liver and lung d21 n=4, d50 n=6, d100 n=7; data from at least two independently performed experiments). (C) βgal96-specific CD8+ T cells kill peptide loaded target cells. Splenocytes from naïve C57BL/6 mice were stained with cellTrace violet, loaded or not with the βgal96 peptide and transferred i.v. into naïve B6 mice or B6 mice previously immunized (d21, d50 and d100) with Ad-LacZ. FACS analysis of the surviving donor cells in blood, spleen, liver and lung of recipient mice was performed 12 hours later. FACS plots show the transferred splenocytes (cellTrace violet low=control group; cellTrace violet high=βgal96-pulsed target cells) 12h after transfer in blood and spleen. Target cells have been killed efficiently on d21, d50 and d100. (D) % Specific killing of βgal96- (black circles) or βgal497-(white squares) target cells in blood, spleen, liver and lung was measured 12h after adoptive transfer by FACS analysis in d0, d21, d50 and d100 recipient mice. Mean percentage of specific killing is indicated (±SEM; spleen, blood, liver and lung d21 n=6, d50 n=6, d100 n=8; data from three independently performed experiments).
