Figure 1. Loss of AR promotes metastasis with poorer prognosis in DEN-HCC mice.
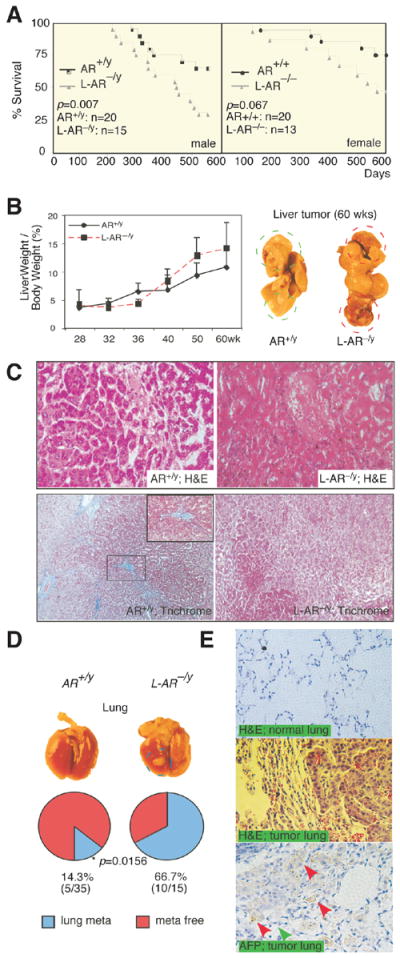
(A) Cancer survival of the male and female ARKO and L-ARKO mice. Mantel-Haenszel log-rank test of ARKO versus L-ARKO HCC mice survival in male (AR+/y and L-AR−/y, left panel) and female (AR+/+ and L-AR−/−, right panel). Comparing ARKO and L-ARKO P= 0.007 while it is 0.067 in female. (B) Liver weight/body weight (LW/BW) of HCC tumors in 28-, 32-, 36-, 40-, 50-, and 60-wks old mice. 28-wks old tumors from each genotype were set as basal level for comparisons (left panel). Gross observation on 60-wks old HCC mice (right panel). AR+/y (WildType mice); L-AR−/y (Liver specific AR knockout mice). (C) More malignant Histological pattern of 60-wks HCC tumors in L-AR−/y than in AR+/y mice. H&E staining (upper panel; 400X), and Trichrome stain (lower panel; 200X). Blue color indicates ECM deposition. (D) Gross observation of the lungs from AR+/y and L-AR−/y mice at 60-wks (upper panel). Percent of lung metastasis vs. normal lung occurring in the AR+/y and L-AR−/y mice at 60-wks old HCC tumors (lower panel). * P value indicated a statistical significance by Fisher test. (E) Histological study of the lungs from mice with 60-wks old metastatic HCC tumors. Upper panel: H&E staining of normal lung in L-AR−/y mice. Middle panel: H&E staining of metastatic tumor in L-AR−/y mouse lung. Lower panel: α-fetoprotein (AFP) staining of metastatic tumor of L-AR−/y mice lung. Red arrows indicate positive AFP staining of metastatic liver tumor cells. Green arrow indicates negative AFP staining of normal lung aveoli epithelia.
