Figure 2. Loss of AR leads to increased p38 phosphorylation, and reduced anoikis.
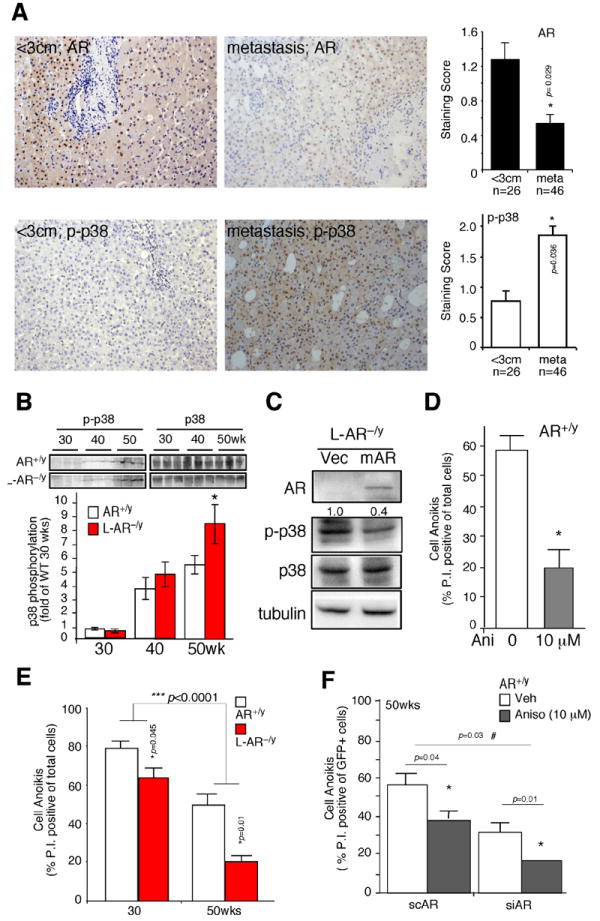
(A) AR and phospho-p38 (p-p38) expression in human HCC. The Immunohistochemistry staining of AR and p-p38 expression in tumors less than 3cm, and metastatic tumors. The quantitative results of AR and p-p38 based on staining scoring (ranking 0~3) in slides reviewed by two independent board certified pathologists. * indicates p-value significantly different (<0.05) comparing two groups. (B) Phospho-p38 (p-p38) and total p38 expression in HCC tumors of 30-, 40-, and 50-wks old mice (upper panel). The lower panel is the band densitometry quantitation of p-p38/p38 of AR+/y (n=6) and L-AR−/y mice (n=7) at each time point. Mean value of HCC in 30-wks old AR+/y mice was set as basal and compared. (C) Lentiviral transduction of vector (Vec) and mouse AR cDNA (mAR) in the hepatic cells from L-AR−/y HCC. Twenty μg total protein was loaded for SDS-PAGE, and Immunoblots were used to detect the protein levels of AR, p-p38, p38, and tubulin. (D) Anoikis was observed in the hepatic cultured cells from AR+/y mice treated with the p38 agonist, anisomycin (10 μM). (E) Cell anoikis was observed using hepatic culture cells from liver tumors of 30- and 50-wks old AR+/y and L-AR−/y mice. (F) Cell anoikis was measured in the primary hepatic cells from AR+/y, with introduced lentiviral-based AR scramble RNA (scAR) or small interference (siRNA), and treated with/without Anisomycin 10 μM (left panel). All the animal experiments were confirmed in at least three pairs of WT and LARKO littermates. Anoikis data were collected from three individual sets of experiments, and standard deviation (SD) was applied to represent error bars. * Represents significant difference with p-value <0.05.
