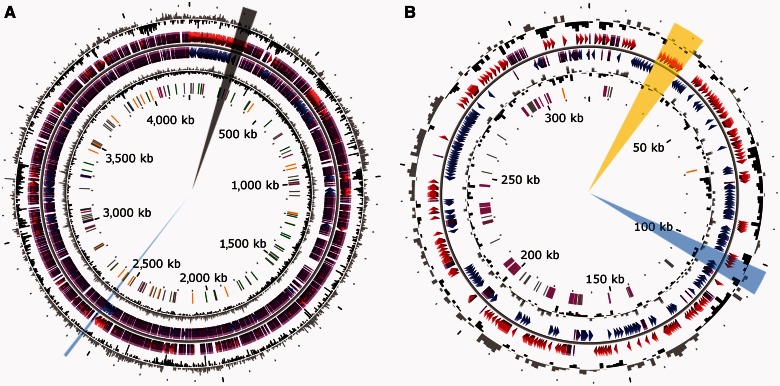
Fig. 1.—
Circular representation of the Rhizobium sp. NT-26 genome. The chromosomal (A) and plasmidic (B) characteristics are 4,239-Mb long, 61.97% GC, 9 16S-23S-5S rRNA, 50 tRNA, and 4,294 CDSs; and 322-kb long, 60.19% GC, 0 16S-23S-5S rRNA, 0 tRNA, and 367 CDSs, respectively. From outside, circles display 1) the GC percent deviation in a 1,000 bp window (GC window – mean GC); 2) and 3) predicted CDSs transcribed in the clockwise and counterclockwise direction, respectively; red and blue colors correspond to validated annotations, orange to automatic annotation and purple to primary automatic annotation; 4) GC skew (G + C/G − C) in a 1,000 bp window; 5) rRNA are shown in blue, tRNA in green, miscRNA in orange, transposable elements in pink, and pseudogenes in gray. The regions with the genes coding for proteins involved in motility, reduction of arsenate or oxidation of arsenite are highlighted in black, blue, or yellow, respectively. The figure does not represent the p2 plasmid and the scale between the two genetic determinants is not respected (https://www.genoscope.cns.fr/agc/microscope/home/index.php, last accessed April 30, 2013).