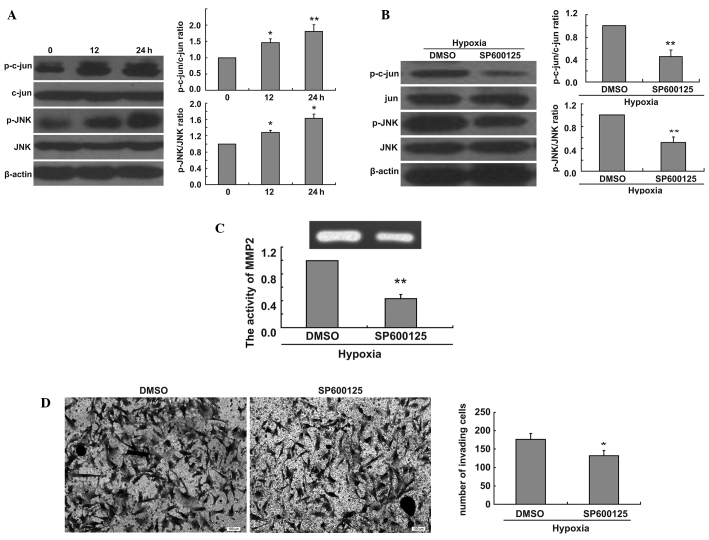
Figure 2.
Inhibition of JNK decreases ratio of p-c-jun/c-jun and p-JNK/JNK, MMP2 activity and glioma cell invasion in hypoxic conditions. (A) Western blot analysis shows the time-dependent effect of hypoxia on ratio of p-jun/jun and p-JNK/JNK in U251 cells. The bar graph shows relative ratio of p-jun/jun and p-JNK/JNK in hypoxia-treated cells versus those in control cells (*P<0.05, **P<0.01). (B) Western blot analysis shows ratio of p-jun/jun and p-JNK/JNK in U251 cells treated with 30 μmol/l SP600125 in hypoxic conditions for 24h. The bar graph shows relative ratio of p-c-jun/c-jun and p-JNK/JNK in JNK inhibitor-treated cells versus those in control cells (**P<0.01). (C) U251 cells treated with 30 μmol/l SP600125 were incubated in hypoxic conditions for 24 h and cell culture medium samples were collected. Gelatin zymography assays show the effect of SP600125 on enzymatic activity of MMP2 under hypoxic conditions. The bar graph shows the relative integrated densities of the bands in treated cells versus those in control cells (**P<0.01). (D) U251 cells treated with 30 μmol/l SP600125 were incubated in a Transwell chamber in hypoxic conditions for 24 h, and the cells were stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. The bar graph shows mean number of migrated cells (*P<0.05).