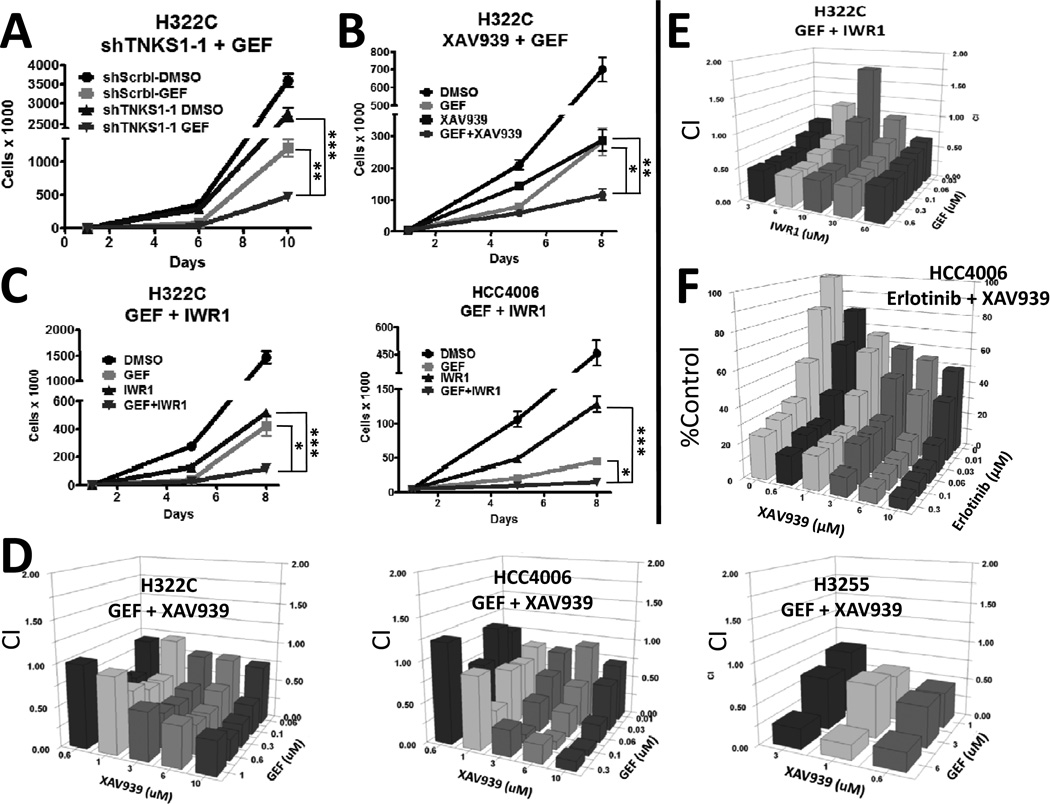
FIGURE 2. Combined inhibition of EGFR and tankyrase leads to synergistic inhibition of NSCLC cells.
A) H322C cells expressing either negative control shRNA (shScrbl) or shRNAs targeting TNKS1 (TNKS1-1) were treated in triplicate with vehicle (DMSO) or 500 nM gefitinib (GEF) for 4 days, followed by replating without drug for 4 more days. Viable cells were counted by flow cytometry using PI-exclusion. B) H322C cells were treated in triplicate with DMSO or 500 nM gefitinib and/or the TNKS inhibitor XAV939 (5 µM) for 4 days, and then replated without drugs for 3 additional days. Viable cells were counted. C) H322C and HCC4006 cells were treated in triplicate with DMSO or gefitinib (500 nM for H322C or 20 nM for HCC4006) and/or the TNKS inhibitor endo-IWR1 (IWR1; 20 µM) for 4 days, and then replated without drugs for 3 days. Viable cells were counted. For A–C, * indicates p<0.05, ** p<0.01, and *** p<0.001. D) The indicated NSCLC cell lines were treated in triplicate with DMSO, gefitinib and/or XAV939 at the indicated concentrations for 5 days, and cell viability assessed by MTT assays. Graphs were plotted for Combination Indices (CI) using to determine additivity (CI=1), synergism (CI<1) and antagonism (CI>1). E) As in D, H322C cells were treated in triplicate with DMSO, gefitinib and/or endo-IWR1. F) HCC4006 cells were treated in triplicate with DMSO, erlotinib and/or XAV939 as in D. Graph was plotted in comparison to untreated cells.