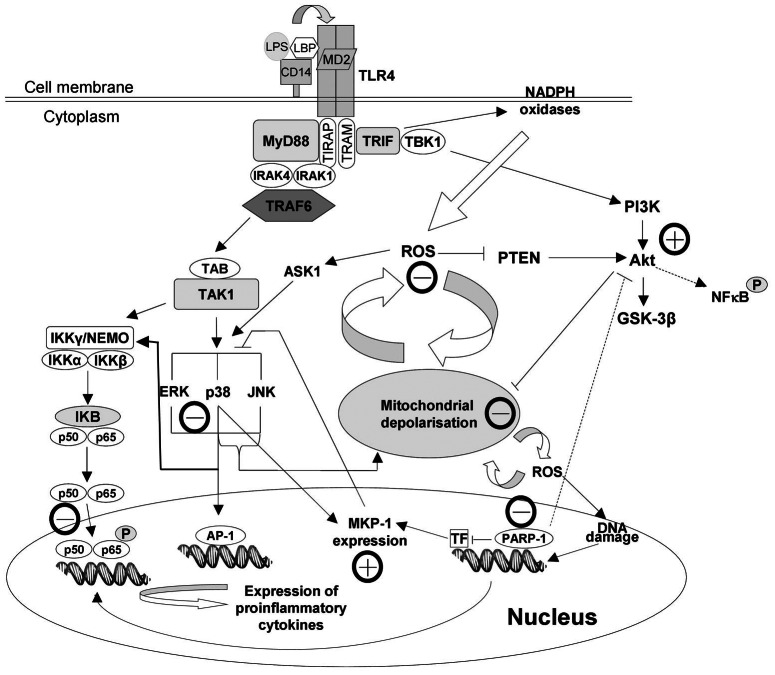
Figure 10. Effect of malvidin on LPS induced pathophysiological changes in RAW 264.7 macrophages.
Well documented effects are indicated by solid lines, whereas effects involving yet unidentified mediator(s) or events are represented by dashed line. Lines with pointed end denote activation, whereas lines with a flat end indicate inhibition. Activating or inhibitory effect of malvidin is indicated by a circled + or − next to the line, respectively. LPS induces activating phosphorylation, nuclear translocation and DNA binding of NFκB, induction of ROS production, PARP activation, activation of MAPKs, MKP-1 expression, activation of the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase-Akt pathway and destabilization of the mitochondrial membrane systems. Malvidin attenuates ROS production, mitochondrial destabilization, and activation of PARP and MAPKs. It also augments Akt activation and MKP-1 expression resulting in diminished activation of NFκB. AP-1: activator protein-1; Akt: Protein Kinase B (PKB); Ask1: apoptotic signal regulating kinase; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; GSK-3β: Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; IκB: inhibitors of NF-κB; IKK: inhibitor of NF-kappa B kinase; IRAK1: interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1; IRAK4: interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-4; JNK: c-jun N-terminal kinase; LBP: LPS binding protein; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; MKP-1: MAPK phosphatase -1; MyD88: myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88; NEMO: NF-κB essential modifier; NF-kappa B: nuclear factor kappa B; P: phosphorylated; PARP: poly-(ADP-ribose) polymerase; p65: Transcription factor p65 (RelA); p50: NF-KappaB1; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PTEN: phosphatase and tension homolog deleted on chromosome 10; ROS: reactive oxygen species; TAB: TAK1-binding protein; TAK1: transforming growth factor- β-activated kinase 1; TBK1: TANK binding kinase 1; TF: transcription factor; TIR: Toll-interleukin-1 receptor; TIRAP: TIR domain-containing adaptor protein; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; TRAF6: TNF receptor-associated factor 6; TRAM: TRIF-related adaptor molecule; TRIF: TIR domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-β.