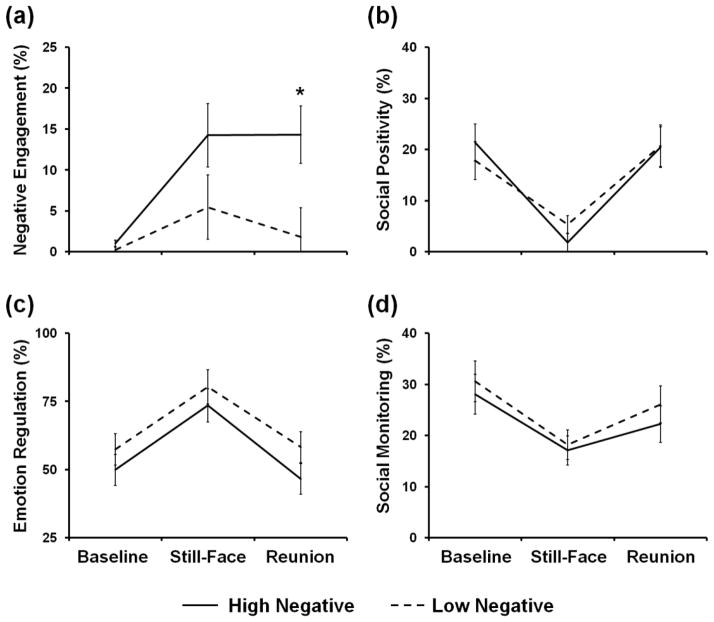
Figure 1.
Effects of negative reactivity on infants’ behavior during the still-face paradigm. (a) Infants reported as having high levels of temperamental negative reactivity (high negative, solid line) displayed negative engagement behaviors more often during the reunion phase compared to infants reported as having low levels of temperamental negative reactivity (low negative, dashed line). High and low negative infants did not differ on displays of (b) social positivity, (c) emotion regulation, or (d) social monitoring. * p<0.05.