Figure 2.
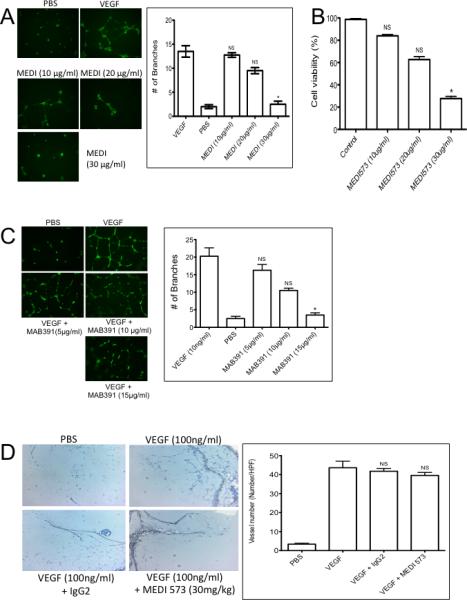
A. MEDI-573 inhibits HUVEC tube formation and proliferation in vitro. A. HUVECs were grown under serum-deficient conditions and stimulated with PBS or VEGF (10 ng/ml) in the absence or presence of MEDI-573 (10, 20 or 30 μg/ml). Tubes were visualized by staining with Calcein AM dye. Tube formation was quantified as described in Materials and Methods. B. Proliferation/viability was determined after 2 days by alamar blue (AB) staining. C. Mab391 inhibits HUVEC tube formation in vitro. HUVECs were grown under serum-deficient conditions and stimulated with VEGF (10 ng/ml) in the absence or presence of MAB391 (5, 10, 15 μg/ml). Tubes were visualized by staining with Calcein AM dye. D. Effect of MEDI-573 in murine angiogenesis in vivo. Matrigel plugs containing with PBS, or VEGF (100 ng/ml) were implanted subcutaneously in mice that were or were not treated with MEDI-573 (30 mg/kg day 0 and day 3). The Matrigel plugs were excised on day 7, fixed with formalin and 5-μm sections were stained with H&E, Messon Trichrome and CD34 staining. The numbers of CD34 positive vessels per high-power field (magnification, 200X) were counted for each experimental condition. Left panels, photomicrographs showing CD34 staining; Right panel: Results are mean (n =5) ± SE. *P <0.05; **P <0.01 versus VEGF alone. Right panel, quantitation of vessels. Mean ± SE. (Six HP fields counted).
