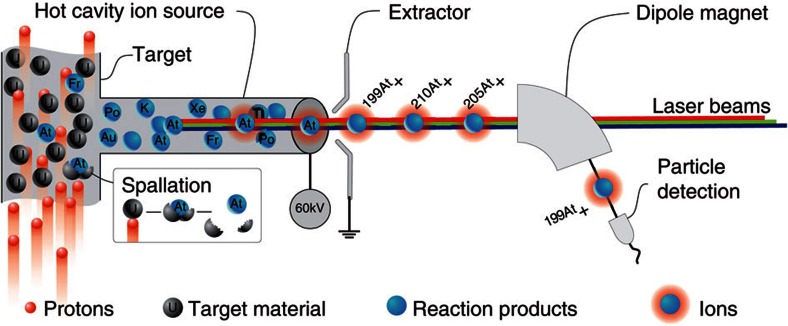
Figure 4. In-source laser spectroscopy at ISOLDE.
Protons impinge on a thick target inducing nuclear reactions (for example, spallation) in which different isotopes of various chemical elements are produced. The reaction products diffuse and effuse towards the hot cavity ion source, into which the precisely tuned laser beams are focussed. Step-wise resonance laser ionization creates singly charged ions of the desired element. These photo-ions are extracted and accelerated by applying a high-voltage potential. The ion beam of the isotope of interest is selected by dipole magnets and guided to a suitable detection setup.