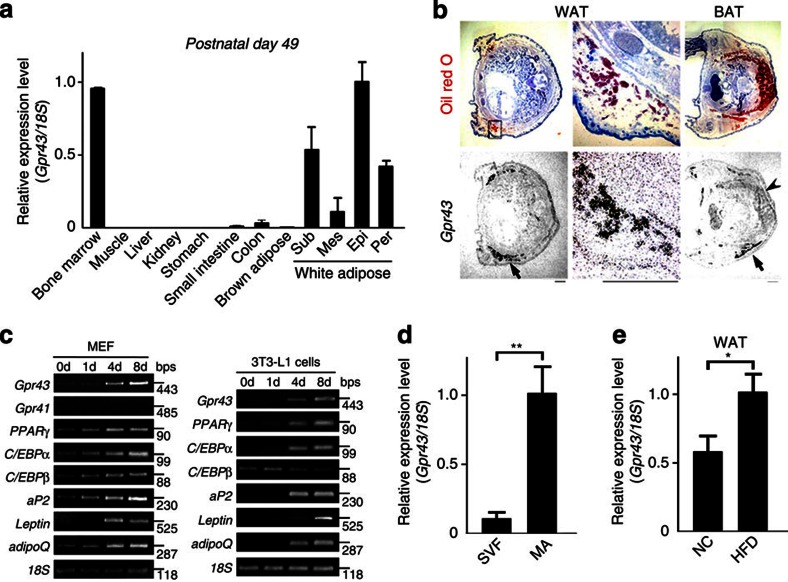
Figure 1. Gpr43 is abundantly expressed in the WATs.
(a) Gpr43 expression in postnatal mouse tissues (P49) measured by qRT-PCR (n=3). Internal control: 18S rRNA expression. (b) Gpr43 mRNA localization in mouse embryos (P1) as determined by in situ hybridization using an 35S-labelled antisense Gpr43 RNA probe. Black grains superimposed on haematoxylin−eosin (H&E) and oil red O-stained sections indicate Gpr43 mRNA localization. Arrow indicates WAT; arrowhead indicates BAT. Scale bar, 1 mm. (c) Expression of Gpr43 mRNA during differentiation. MEF and 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes were induced to differentiate in the presence of MDI. Total RNA was analysed by RT-PCR. 18S was used as a loading control. (d) Gpr43 expression in stromal vascular fraction (SVF) and MAs measured by qRT-PCR (n=3). 18S was used as a loading control. (e) Gpr43 expression in the WAT of NC and HFD-fed mice measured by qRT-PCR (n=4); 18S was used as a loading control. Mice were analysed at 16 weeks of age (d, e). All data are presented as mean±s.e.m. Student’s t-test; *P<0.05; **P<0.005. Epi, epididymal; Mes, mesenteric; Per, perirenal; Sub, subcutaneous.