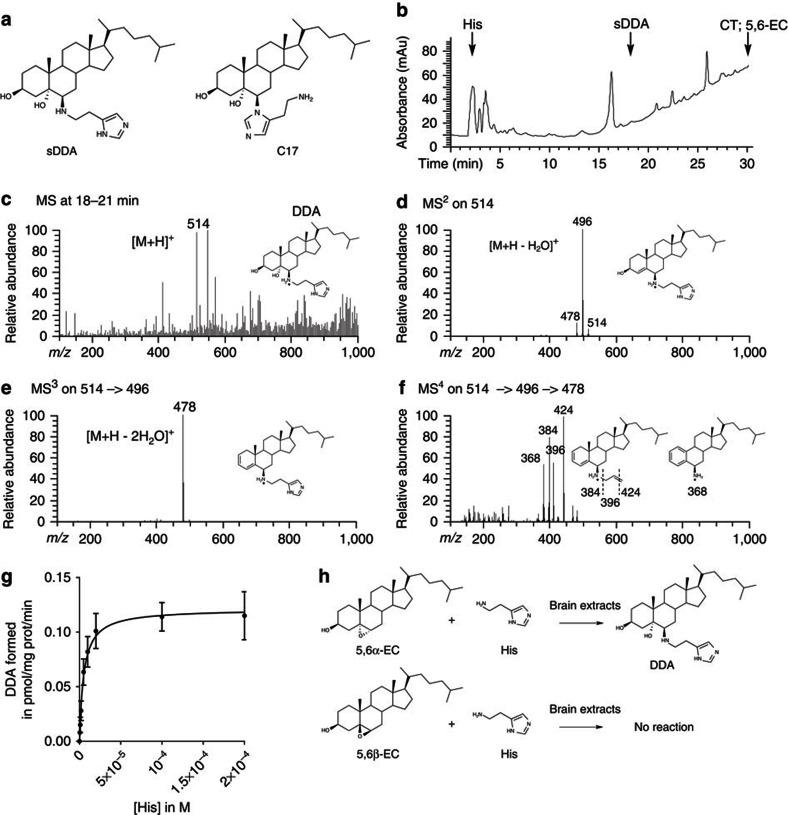
Figure 1. Characterization and formation of DDA in mouse brain homogenates.
(a) Chemical structure of sDDA and synthetic C17. (b) HPLC profile from a total mouse brain extract. The extraction of sterols and HPLC separation were carried out as described in the ‘Methods’ section. Arrows indicate peaks corresponding to the authentic standards: His, sDDA, CT and 5,6-EC. The fractions collected between 18 and 21 min from HPLC purification of the mice brain extract were submitted to nano-electrospray ionization MS fragmentation. DDA (m/z 514) and deuterated d7-DDA (m/z 521) were fragmented simultaneously using the following parameters: parent ion mass, m/z 518; parent ion isolation width, m/z 8; and collision energy, 33%. MS3 analysis of the DDA and d7-DDA fragments at m/z 496 (Supplementary Fig. S2) and 503 (Supplementary Fig. S5) was performed using the following parameters: parent ion mass, m/z 500; parent ion isolation width, m/z 8; and collision energy, 45%. MS4 analysis of the DDA and d7-DDA fragments at m/z 478 and 485 was performed using the following parameters: parent ion mass, m/z 482; parent ion isolation width, 8 m/z; and collision energy, 50%. MS4 quantification of DDA was calculated from the m/z 424/431 ratio obtained by averaging 100 spectra. (c) (MS1) resulted in a molecular ion of [M+H]+ (m/z 514) obtained in MS1. (d) MS2 fragmentation of the [M+H]+ (m/z 514). (e) MS3 fragmentation of the (m/z 496) peak obtained in MS2. (f) MS4 fragmentation of the (m/z 478) peak obtained in MS3. (g) Michaelis–Menten plot of DDA formation. 2 μM of [14C]-5,6α-EC and His (0.5–200 μM) were incubated 10 min at 37 °C in the presence of mouse brain homogenate. Lipids were extracted and analysed by thin-layer chromatography, and DDA was quantified as described in the ‘Methods’ section. Experiments were repeated at least three times in duplicates. The data presented are the means±s.e.m. of all experiments. (h) Schemes describing the transformation of 5,6α-EC and 5,6β-EC in the presence of His and brain extracts.