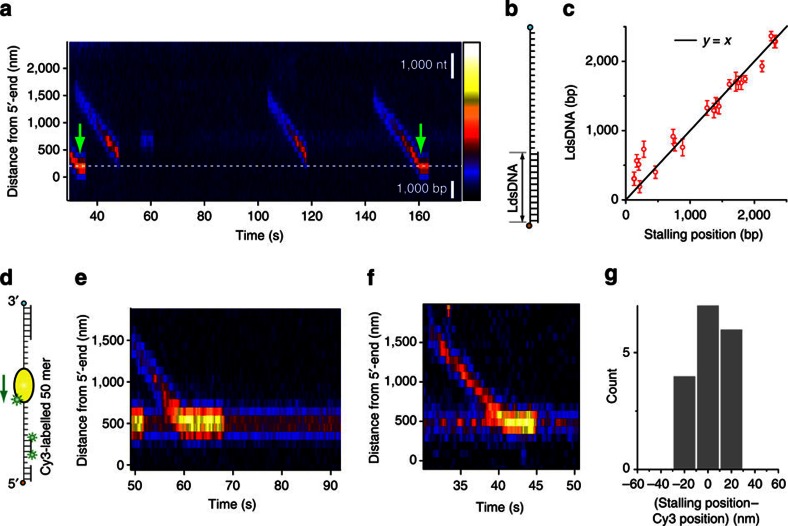
Figure 4. UvrD translocation is blocked by dsDNA.
(a) A kymogram showing stalling of UvrD. There is a certain location on a DNA where UvrD stops its translocation and stalls (green arrows). The stalling position is close to the white dashed line, which indicates the position of ssDNA/dsDNA junction (the length of duplex segment estimated from fitting the force–extension curve to the model). Scale bars correspond to the length of 1,000 nt (ssDNA) and 1,000 bp (dsDNA), respectively. (b) A partial duplex DNA construct used in the experiment is shown here. The length of duplex segment is estimated by fitting the force–extension curve to a polymer model. (c) The correlation between the length of duplex segment (the position of the junction) and the distance of the stalling position from the 5′-end of the tracking strand in the DNA constructs. The error bar represents the standard error. The scatter plot follows the identity relation (y=x, R2=0.95), which suggests that the stalling occurs at the ssDNA/dsDNA junction. (d) Another experiment designed to measure the location of ssDNA/dsDNA junction more directly. An additional ssDNA/dsDNA junction is created by annealing a fluorophore-labelled oligonucleotide to the tracking strand. We doubly labelled the oligonucleotide by way of precaution against fluorophore photobleaching. (e) A kymogram of a translocating UvrD monomer, eventually blocked by the presence of duplex region created by a complementary oligonucleotide annealed to the tracking strand. At ~52 s, one of the two fluorophores on the complementary oligonucleotide photobleaches, but the remaining Cy3 fluorophore marks the location of duplex region until the end of the kymogram. (f) Another kymogram showing UvrD stalling events. Here as well, translocation stops at the position of Cy3 fluorescence. (g) The distribution of the difference between stalling position and Cy3 position (the position of ssDNA/dsDNA junction) for 17 stalling events.