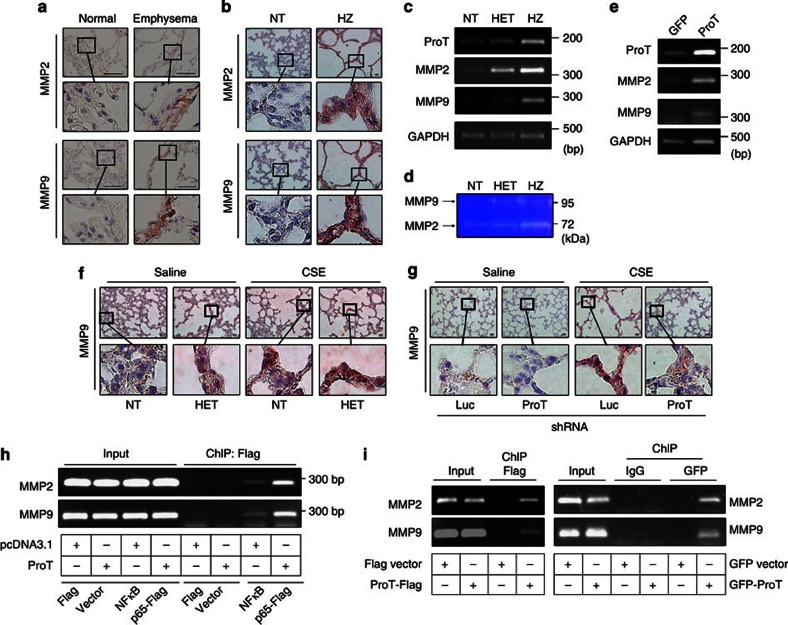
Figure 7. ProT upregulates the production of MMP2 and MMP9 in emphysematous lungs of mice and patients.
(a,b) Immunohistochemical detection of MMP2 and MMP9 in lung tissues from patients with emphysema and non-COPD individuals (Scale bar=100 μm) (a) and from ProT HET and NT mice (Scale bar=20 μm) (b). (c,e) Expression of MMP2, MMP9, ProT and GAPDH (serving as the loading control) mRNA in lung tissues of 4-day-old ProT HZ, HET and NT mice (c) and in 293 T cells transduced with lentiviral vectors Lenti-ProT or Lenti-GFP (e), as analysed by RT–PCR. (d) Gelatin zymography of MMP2 and MMP9 in the conditioned medium of mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) from ProT transgenic and NT mice. (f,g) Immunohistochemical detection of MMP9 in lung tissues (Scale bar=20 μm) from ProT HET and NT mice injected intraperitoneally with CSE or saline twice a week for 6 weeks (f) and from FVB mice that had been intratracheally injected with lentiviral vectors expressing ProT or luciferase (Luc) shRNA followed by intraperitoneal injections of CSE or saline twice a week for 6 weeks (g). The boxed areas in upper panels (× 400) are magnified and shown in lower panels (a,b,f,g). (h) ChIP analysis showing increases in NF-κB binding to MMP2 and MMP9 promoters by ProT overexpression. 293T cells that had been transfected with pcDNA3.1-ProT-myc/His or pcDNA3.1 were cotransfected with Flag-tagged NF-κB p65 expression vector or a control vector. Cross-linked chromatin was immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag-M2 beads and then amplified for the MMP2 or MMP9 gene region containing the NF-κB binding site. Cell lysates without immunoprecipitation (input) were estimated for chromatin containing MMP2 or MMP9 gene region. (i) ChIP analysis showing direct binding of ProT to the NF-κB-binding site-containing region of MMP2 and MMP9 promoters. 293T cells were transfected with plasmid Flag-tagged ProT (pCMV-Tag4A-ProT) or Flag control vector (left) or GFP-tagged ProT or GFP alone (right). Cross-linked chromatin was immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag-M2 beads (left) or anti-GFP or anti-IgG antibody combined with protein A plus G sepharose (right) followed by amplification of the MMP2 or MMP9 gene region containing NF-κB binding sites. Results are representative of three independent experiments.