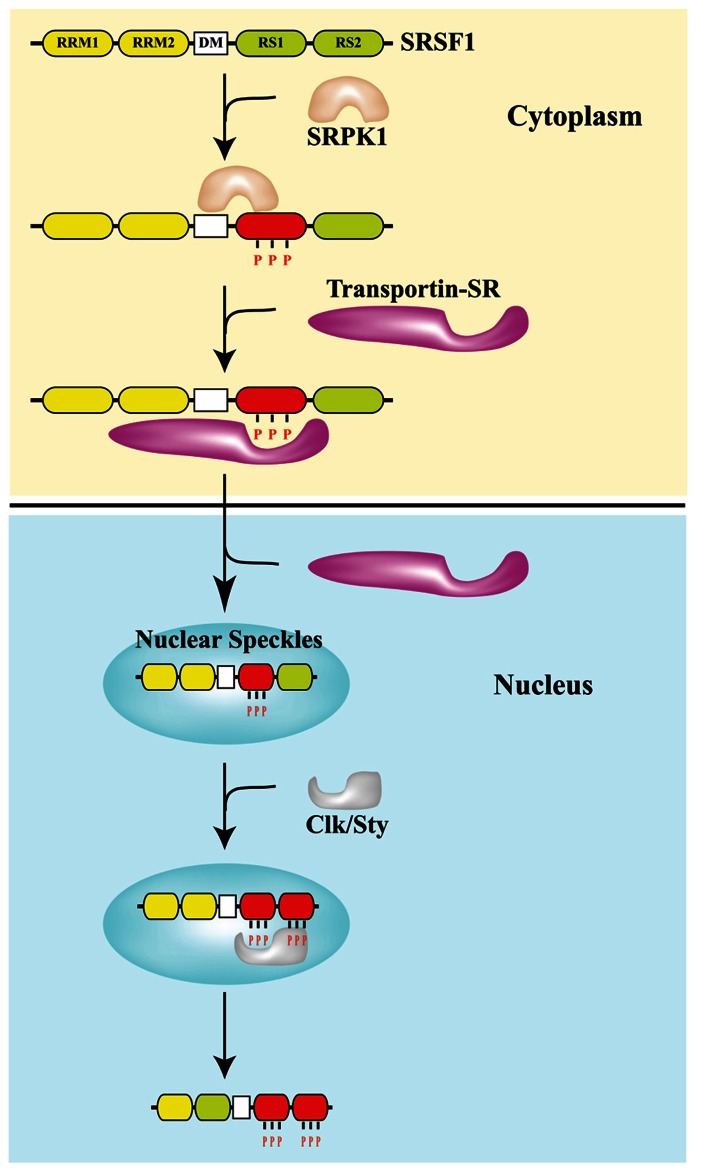
FIGURE 2.
DNA damage affects splicing decisions by modulating the phosphorylation status of RNAPII and the elongation rate of transcription. CPT-induced Top1ccs have immediate and specific effects on RNAPII. CPT triggers a high degree of phosphorylation of the largest subunit (Rpb1) of RNAPII (Baranello et al., 2010). Ultraviolet (UV) irradiation affects cotranscriptional alternative splicing in a p53-independent manner, through hyperphosphorylation of the RNAPII carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) and subsequent inhibition of transcriptional elongation (Muñoz et al., 2009).