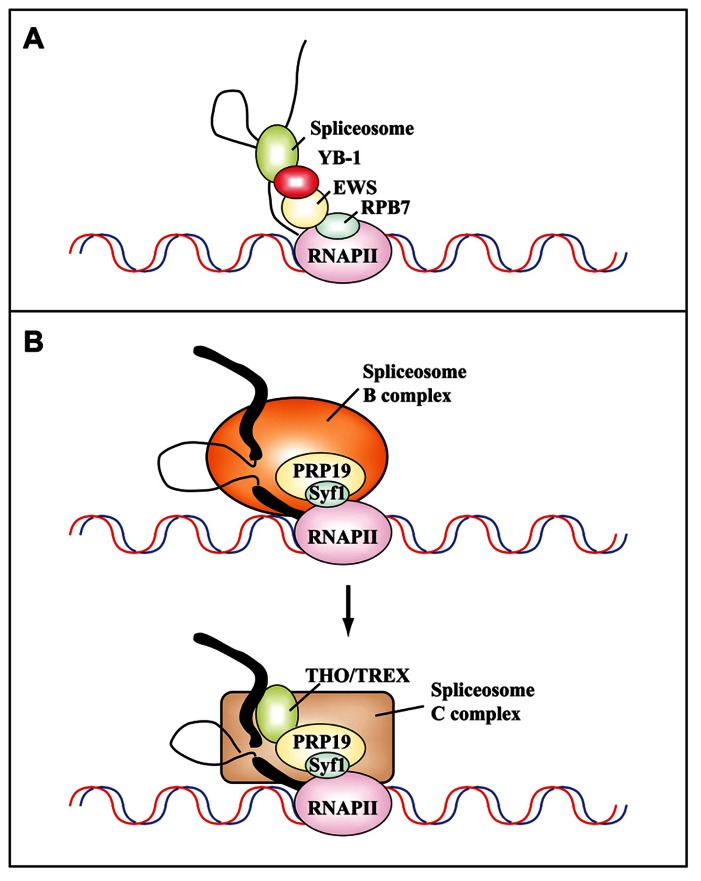
FIGURE 3.
Protein–protein interactions mediate the cotranscriptional assembly of ribonucleoprotein complexes that are targets of DNA damage-induced signaling pathways. (A) Schematic representation of the communication between the transcriptional and splicing machineries mediated by RPB7, EWS, and YB-1. Camptothecin inhibits the interaction between Ewing’s sarcoma proto-oncoprotein (EWS), an RNAPII-associated factor, and YB-1, a spliceosome-associated factor. This results in the cotranscriptional skipping of several exons of the MDM2 gene (Dutertre et al., 2010). (B) The PRP19 complex functions in transcription and is recruited to the transcription machinery by the C terminus of its component Syf1, the yeast homolog of human XAB2 (adapted from Chanarat et al., 2011). Human XAB2 co-purifies both with factors involved in transcription (RNAPII), splicing (PRP19), and TCR (XPA, CSA and CSB; Kuraoka et al., 2008). The PRP19 complex is required for the recruitment of the THO/TREX complex to nascent transcripts after the switch from the B to the C splicing complex. Thick and thin black lines represent exons and introns, respectively.