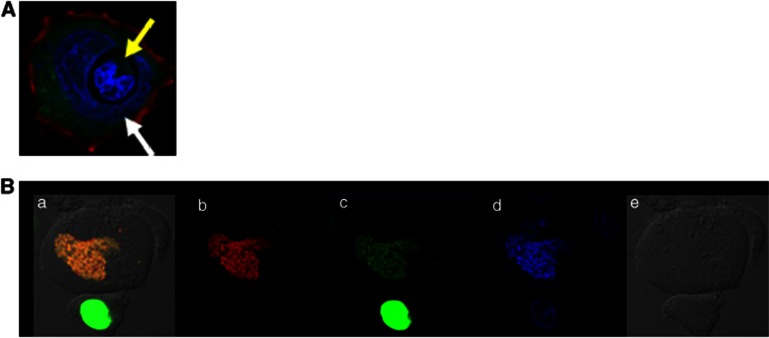
Figure 1.
Nucleus penetration and nucleus fusion after cell-in-cell interaction. (A) Nucleus penetration One lymphocyte (yellow arrow) penetrates directly into the nucleus of a host cell (white arrow) to form a typical heterotypic cell-in-cell structure. Nucleus is displayed in purple with DAPI (4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) staining. (B) Nucleus fusion One PLC/PRF/5 cell line expressing H2B-EGFP (green, b) is co-cultured with one PLC/PRF/5 cell line expressing H2B-RFP (red, c) for 4 h. DAPI staining is preformed (blue, d) before cell-in-cell structure is observed under differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy (e). Yellow nucleus under DIC image is shown after 4 h (a) probably due to cell fusion of two cells. (Unpublished data)