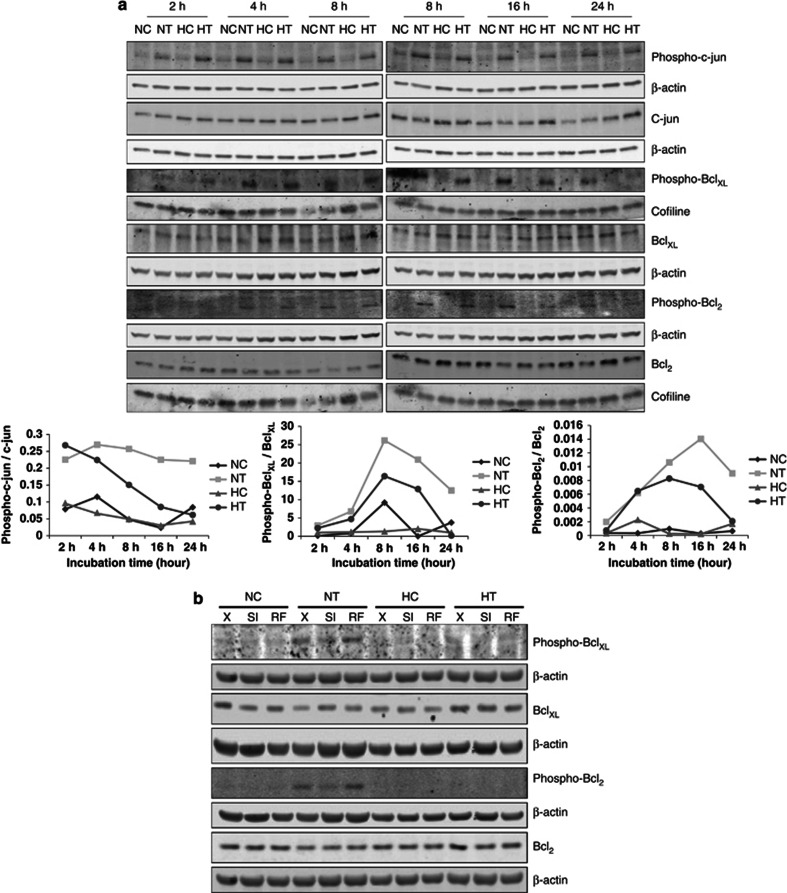
Figure 5.
JNK-dependent phosphorylation of c-jun, Bcl2 and BclXL is induced by taxol but decreased after long incubation time under hypoxia. MDA-MB-231 cells were incubated under normoxia (N) or hypoxia (H) without (C) or with taxol (T) at 50 μM. (a) After 2, 4, 8, 16 and 24 h of incubation, c-jun, Bcl2, BclXL, phospho-c-jun, phospho-Bcl2 and phospho-BclXL were detected in total cell extracts, obtained with a phospho-protein-specific lysis buffer, by western blotting analysis, using specific antibodies. β-actin was used to assess the total amount of proteins loaded on the gel. The graphs below represent the quantification of phospho-c-jun, phospho-Bcl2 and phospho-BclXL abundance normalized to β-actin relative to c-jun, Bcl2 and BclXL total abundance normalized to β-actin. (b) MDA-MB-231 cells were untransfected (X) or transfected with 25 nM of JNK1 and 25 nM of JNK2 siRNA (SI) or negative control RF siRNA at 50 nM (RF) for 24 h. The transfection media were removed and replaced by culture media for 24 h. Cells were then incubated under normoxia (N) or hypoxia (H) for 16 h, without (C) or with taxol (T) at 50 μM. Bcl2, BclXL, phospho-Bcl2, phospho-BclXL were detected in total cell extracts, obtained with a phospho-protein-specific lysis buffer, by western blotting analysis, using specific antibodies. β-actin was used to assess the total amount of proteins loaded on the gel