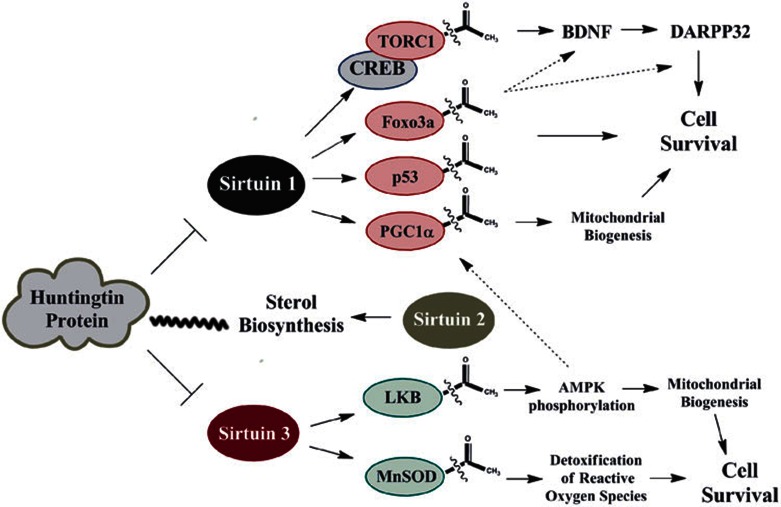
Figure 4.
Sirtuin targets in Huntington's disease. Mutant huntingtin protein can directly inhibit SIRT1 activity, affecting multiple downstream targets. According to one model, SIRT1 deacetylates TORC1, facilitating its interaction with CREB, which is linked to BDNF and DARPP32 expression in neurons10,78,84. Other possible consequences of the inhibition of SIRT1 activity by mutant huntingtin include the decreased deacetylation and altered activities of Foxo3a, p53 and PGC-1α10. In addition, sterol biosynthesis is dysregulated in HD (indicated by the wavy line) and studies using SIRT2 inhibitors have shown decreased neurodegeneration accompanied with decreased sterol biosynthesis in HD models85,86,87,127. It has been proposed that SIRT2 affects cholesterol biosynthetic pathways, which may affect myelination and synapse maintenance in HD mouse models85,86,87. More recently, viniferin, a naturally occurring resveratrol derivative, was shown to be protective in cell culture models of HD. This compound increases SIRT3 levels, affecting LKB and MnSOD acetylation89.