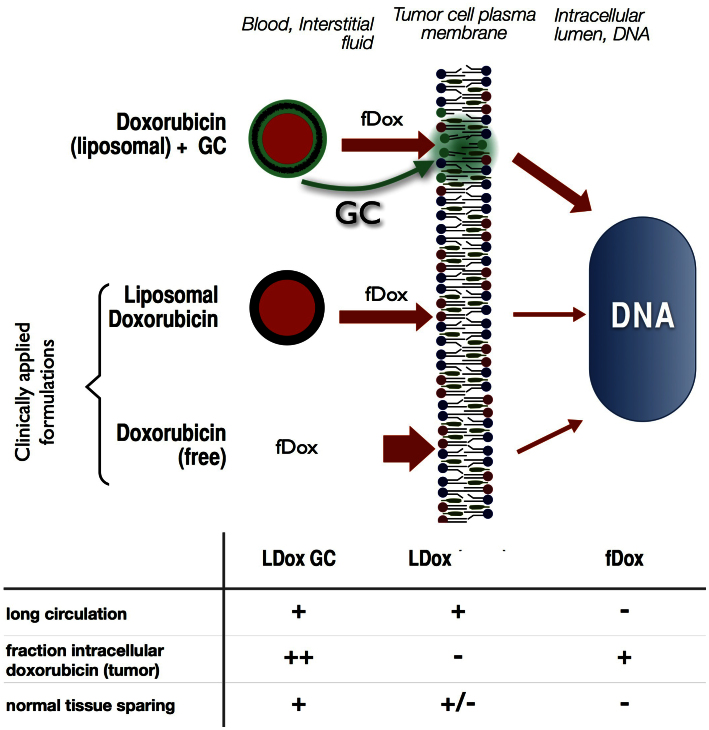
Figure 7. Increased therapeutic window of doxorubicin by GC-mediated membrane modulation.
From the liposomal vehicle, fDox (red) and free GC (green) leak into the interstitial fluids and partition into the (tumour) cell membrane (top cartoon). fDox plasma peak levels are much reduced by liposomal formulation (thinner red arrows left of membrane), but doxorubicin entry in the tumour cell is low in absence of GC (middle cartoon). GC, when co-inserted into the membrane, enhances membrane traversal of doxorubicin (thickened red arrow right of membrane) and thus, accumulation into tumour cell DNA. The relative effects of the three doxorubicin formulations on blood circulation time, tumour cell nucleus incorporation and sparing of normal tissues are summarized in the table.