Figure 1.
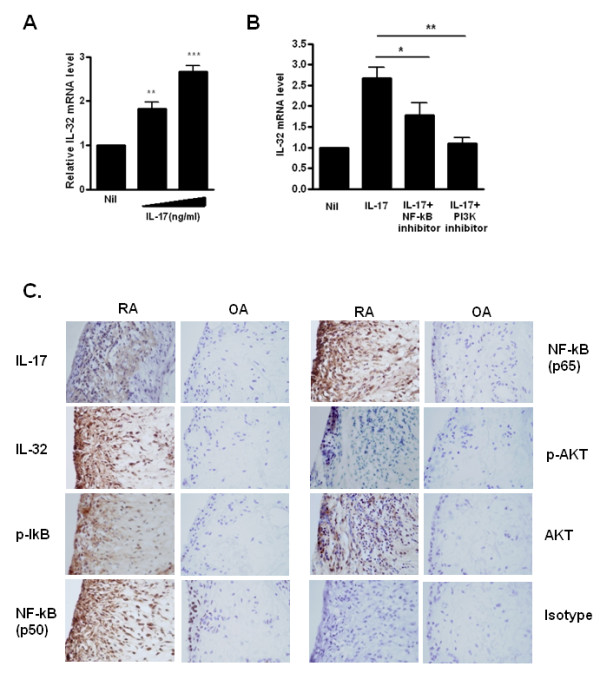
IL-17 induced expression of interleukin (IL)-32 via NF-κB and PI3 kinase in fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) from patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). (A) FLSs from RA patients (RA FLSs) were cultured with increasing doses (1 and 5 ng/ml) of IL-17 for 12 h. IL-32 mRNA levels were measured by real-time PCR. ***P < 0.001 (in comparison with nil), ** P < 0.01 (in comparison with nil). (B) RA FLSs were pretreated with the signal inhibitors parthenolide (10 μM) or LY294002 (10 μM) for 2 h and then cultured with IL-17 (10 ng/ml) for 12 h. The IL-32 mRNA level was measured by real-time PCR. *P < 0.05 (in comparison with IL-17), **P < 0.01 (in comparison with IL-17). A and B show the means ± SD of more than three separate experiments. (C) Expression of IL-17, IL-32, phospho-IkB (p-IkB), NF-κB (p50), NF-κB (p65), phospho-Akt (p-Akt) and AKT in the synovium of patients with RA or osteoarthritis (OA). Immunostaining was performed using specific antibodies. Data are representative of three experiments with similar results.
