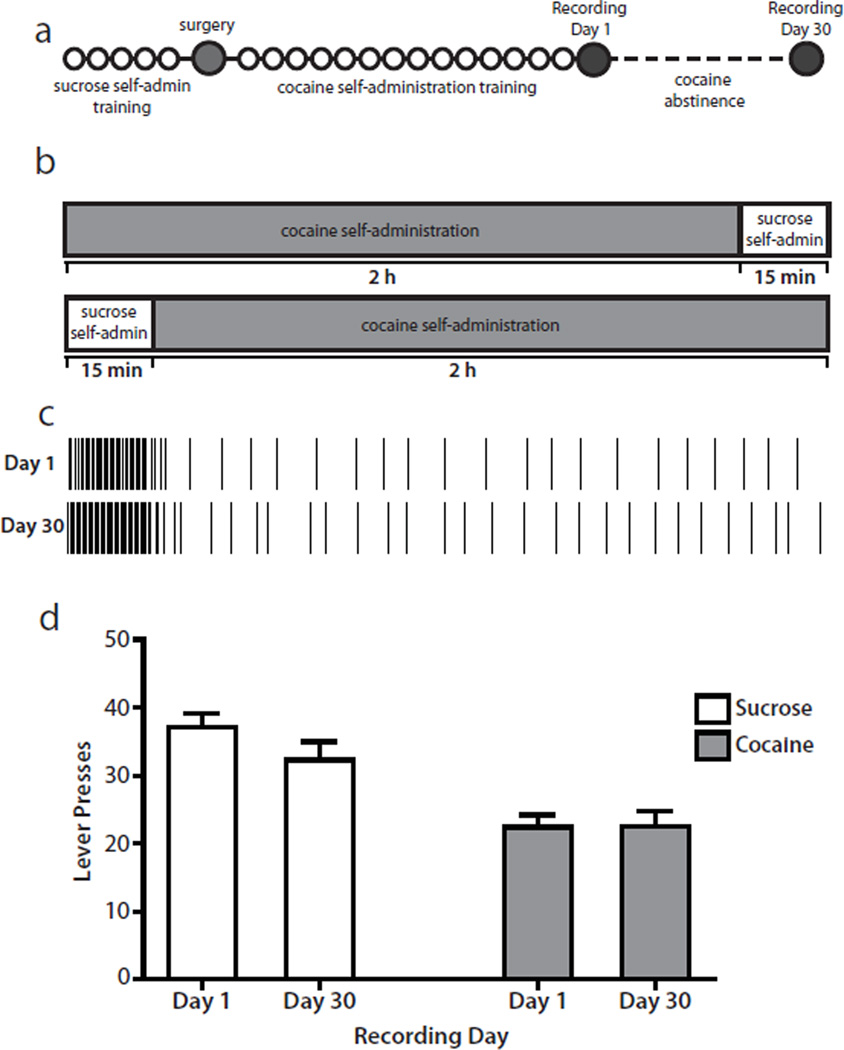
Fig. 1.
Experimental design and behavior. (a) Diagram of the experimental timeline. Each circle represents 1 day. During sucrose self-administration training (~5 days), rats had access only to sucrose during daily 30 min sessions. During cocaine self-administration training (~14 days), rats had access only to cocaine during daily 2 h sessions. On recording Day 1 and Day 30, rats performed a sucrose/cocaine multiple schedule. Cocaine abstinence lasted for 30 days, during which time rats remained in their home cages without drug access. See Materials and methods for details. (b) Schematic diagram of the multiple schedule. On recording Day 1 and Day 30, rats had access to the sucrose-reinforced lever for 15 min followed by access to the cocaine-reinforced lever for 2 h. In a subset of animals, the order of the reinforcers was reversed so that cocaine self-administration preceded sucrose self-administration. See Materials and methods for details. (c) Example of a representative behavioral response pattern for one rat. Each vertical line indicates one lever press response. On Day 1 (top), the rat completed 36 responses on the sucrose lever and 24 responses on the cocaine lever. On Day 30 (bottom), the rat completed 42 responses on the sucrose lever and 30 responses on the cocaine lever. (d) Rats (n=14) displayed consistent numbers of lever press responses across recording sessions (Day 1 and Day 30) for both sucrose and cocaine.