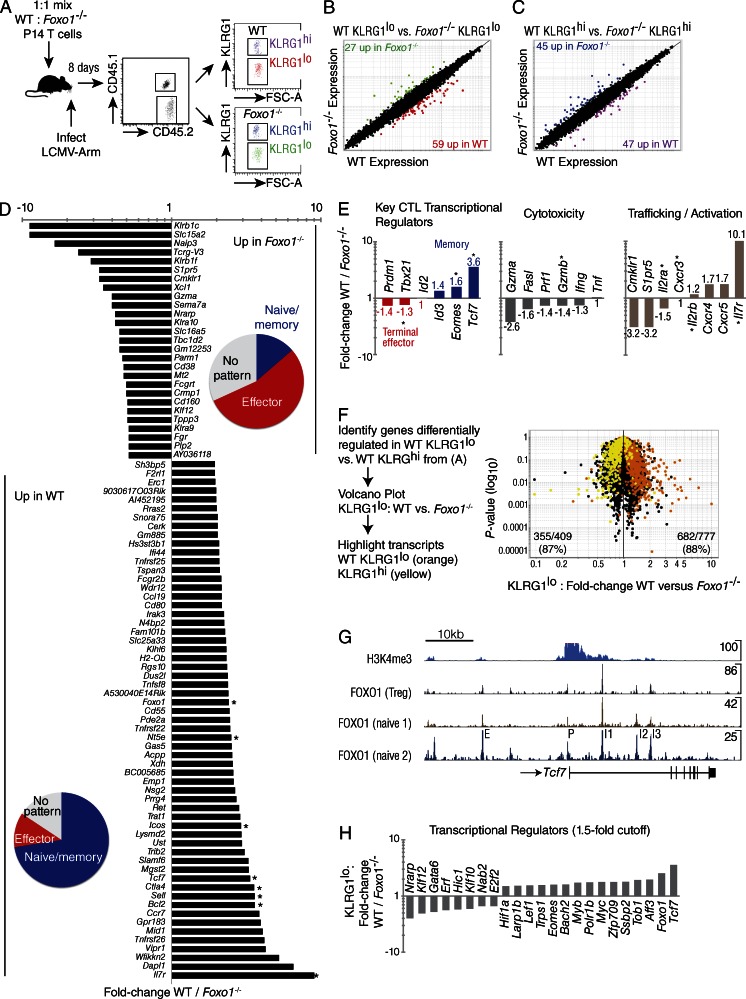
Figure 4.
Deletion of Foxo1 prevents the development of a memory program of gene expression. A 1:1 mix of 104 WT (Foxo1f/f Rosa26) and Foxo1−/− (Foxo1f/f Rosa26Cre-ERT2) P14 cells were prepared from tamoxifen-treated mice and transferred to CD45.1+ WT host mice. Microarray gene-expression analysis was performed by sorting WT and Foxo1−/− KLRG1lo P14 cells 8 d after infection with LCMV-Arm. (A) Experimental scheme for mixed transfer and FACS of WT and Foxo1−/− P14 T cells on day 8 of LCMV-Armstrong infection. The four double-sorted populations were analyzed on the same microarray chip. (B) KLRG1lo WT versus Foxo1−/− reveals 59 genes up and 27 genes down with a twofold cutoff. (C) KLRG1hi WT versus Foxo1−/− reveals 47 genes up and 45 genes down with a twofold cutoff. (D) Identification of genes KLRG1lo WT / Foxo1−/− with a twofold cutoff. Pie charts indicate portion of genes with an expression pattern tied to naive/memory (blue), effector (red), or no pattern (gray). Asterisk indicates expression was verified by flow cytometry. (E) Classification of a subset of the genes in (D) by function. (F) Genes differentially regulated in WT KLRG1lo versus WT KLRG1hi, were overlaid with genes from KLRG1lo WT versus KLRG1lo Foxo1−/− CD8+ T cells, showing nearly a 90% concordance of transcripts. (G) Naive CD4+ ChIP-Seq data showing several FOXO1 binding sites proximal to and within Tcf7. Data were analyzed from T reg cells and two different datasets analyzing naive CD4 T cells. Peaks are labeled as putative: intergenic enhancer (E), promoter (P), and intronic enhancers 1, 2, and 3 (I1, I2, I3). Peak sequences are listed in Table I. (H) Transcription factors known to play a role in the formation of memory cells, summarizing data presented in D with the addition of other transcription factors differentially regulated in WT vs. Foxo1−/− P14 cells. Data are from 1 experiment with n = 3.