Fig. 2.
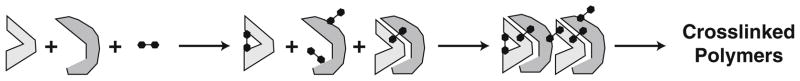
Protein crosslinking. Protein side chains react with bifunctional reagents to form mono-derivatized and cross-linked forms of interacting proteins. Subclasses within each form simultaneously occur through different combinations of mono-derivatization and crosslinking. In the continuous process of crosslinking, conjugates of increasing size may also be formed, progressing from dimers, tetramers, etc. to large extensively crosslinked polymers.
