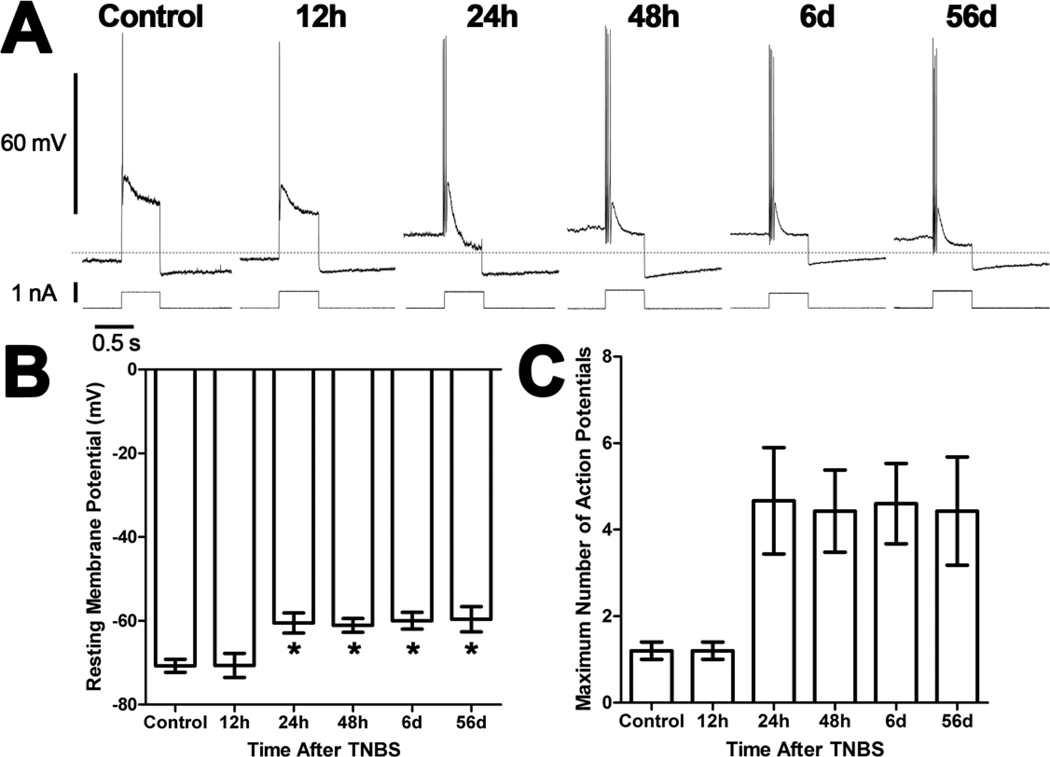
Figure 1. Ileum AH neurons are depolarized and hyperexcitable following TNBS-induced colitis.
A) Representative traces from AH neurons of the guinea pig ileum myenteric plexus illustrating action potentials elicited by 0.5s depolarizing current pulses. All traces are on the same time and voltage or current scales. The dashed line indicates −65 mV. B) A bar graph illustrating the mean (± SEM) resting membrane potential for neurons recorded from each treatment group. Neurons are depolarized from preparations obtained between 24h and 56d after TNBS administration compared to control preparations and preparations 12h after TNBS (*P<0.05 ANOVA Newman-Keuls Multiple Comparison Test). C) A bar graph illustrating the mean (± SEM) maximum number of action potentials for AH neurons recorded from each treatment group. There was a significant difference in the number of action potentials between treatment groups (P<0.05 ANOVA).