Figure 2.
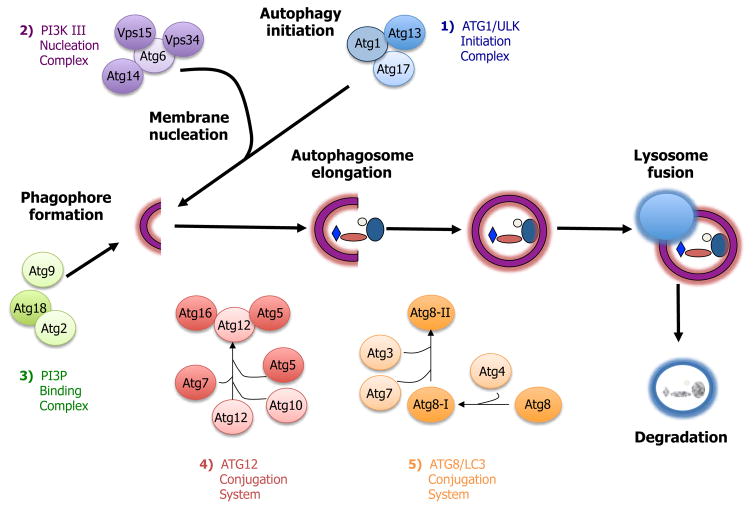
The macroautophagy process. Macroautophagy (here referred to as autophagy) involves a series of steps: autophagy induction, membrane nucleation, phagophore formation, autophagosome elongation, lysosome fusion, and degradation. These steps are controlled by at least five different functional groups of proteins: 1) the Atg1/ULK initiation complex; 2) the PI3-kinase nucleation complex; 3) the PI3P-binding complex, which directs the distribution of Atg9, a transmembrane protein likely important for lipid delivery to the membrane; 4) the Atg5-Atg12 conjugation system; and 5) the Atg8/LC3 conjugation system. In the latter, Atg8 is cleaved by Atg4 to form Atg8-I and is then conjugated with phosphatidylethanolamine to become Atg8-II, which is incorporated into pre- and autophagosomal membranes.