Figure 3. SA pilin subunit structure.
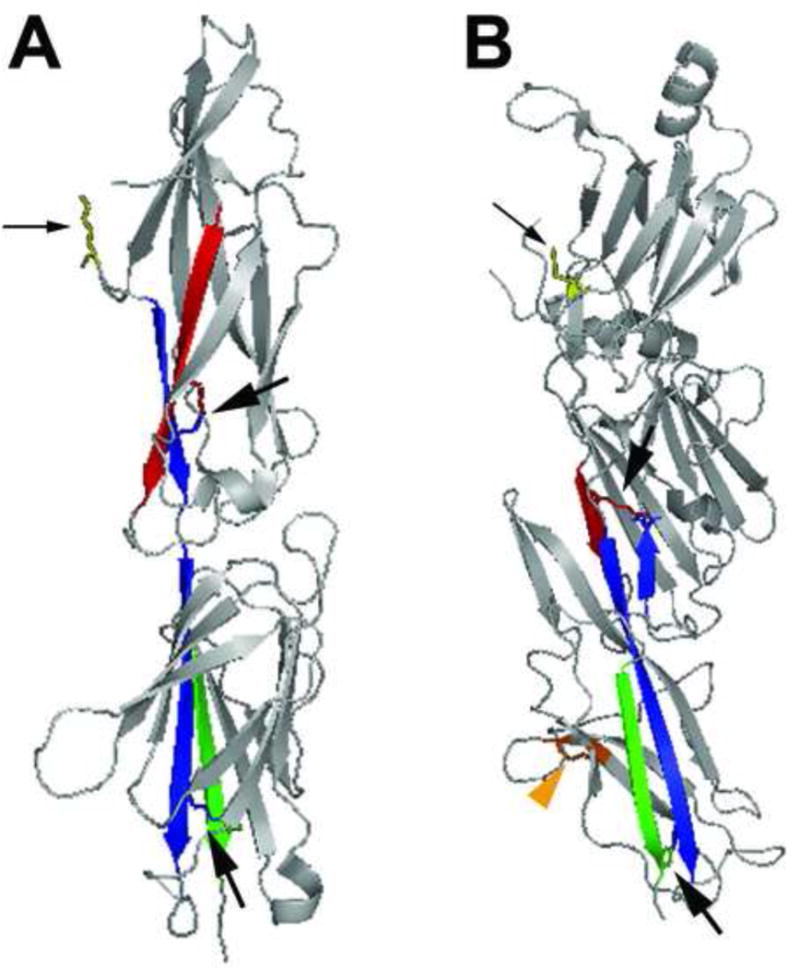
(a) The 32.5 kD two-domain S. pyogenes major pilin subunit structure in ribbon diagram (PDB code 3B2m). The N- and C-terminal β sheets of the molecule are colored red and green, respectively. The interacting β sheet for each amide bond is colored blue. Stick diagrams indicate Lys-Asn intramolecular bonds within each domain of the subunit (indicated by large black arrows) and the conserved lysine (yellow, small black arrow) that becomes covalently linked to the threonine of cleaved LPXTG-like motif in the neighboring subunit. (b) The 47 kD three-domain C. diphtheriae SpaA major pilin subunit structure in ribbon diagram (PDB code 3HR6). The N- and C-terminal β sheets that participate in intramolecular amide bonds are colored red and green (in the middle and C-terminal domain, respectively); the interacting β sheet for each amide bond is colored blue. Stick diagrams indicate Lys-Asn intramolecular bonds within each domain of the subunit (large black arrows), the conserved lysine of the YPKN pilin motif (yellow, small black arrow) that becomes covalently linked to the threonine of cleaved LPXTG motif in the neighboring subunit, and the disulfide bond in the C-terminal domain (orange, orange arrowhead).
