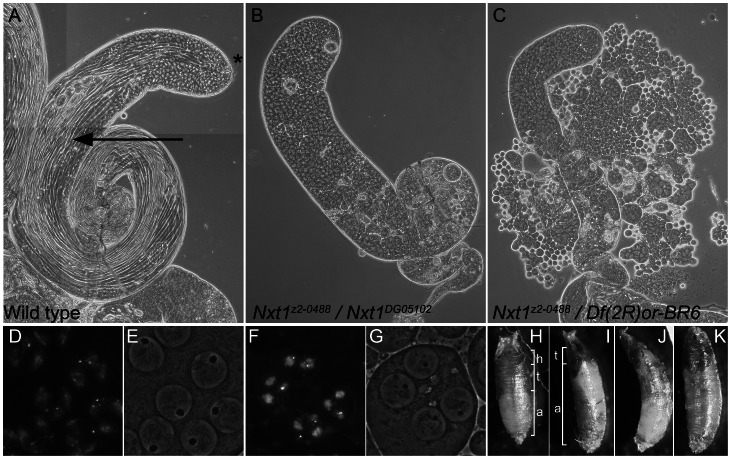
Figure 1. Mutation of Nxt1 leads to meiotic arrest in testes and failure of head eversion in pupae.
(A) All stages of spermatogenesis are seen in wild type testes by phase contrast microscopy. Large round cells near the apical region (*) are primary spermatocytes, while spermatids elongated up the length of the testis (arrow). In Nxt1z2-0488/Nxt1DG05102 mutant (B) or Nxt1z2-0488/Deficiency (C) testes, only stages up to mature primary spermatocytes are present. (D) Hoechst fluorescence and (E) phase contrast images of wild type mature primary spermatocytes reveals a prominent nucleolus and distinct chromosome territories in each nucleus. (F) Hoechst fluorescence and (G) phase contrast imaging of Nxt1 mutant spermatocytes reveals that the cells arrest with partially condensed chromatin and a prominent nucleolus. (H) Nxt1/+ pupae had everted spiracles, and distinct head, thorax and abdomen (h, t, a), while Nxt1 mutant pupae (I–K) often had only partially everted spiracles, and the thorax was at the extreme anterior of the pupal case. Many mutant pupae were also curved (J).