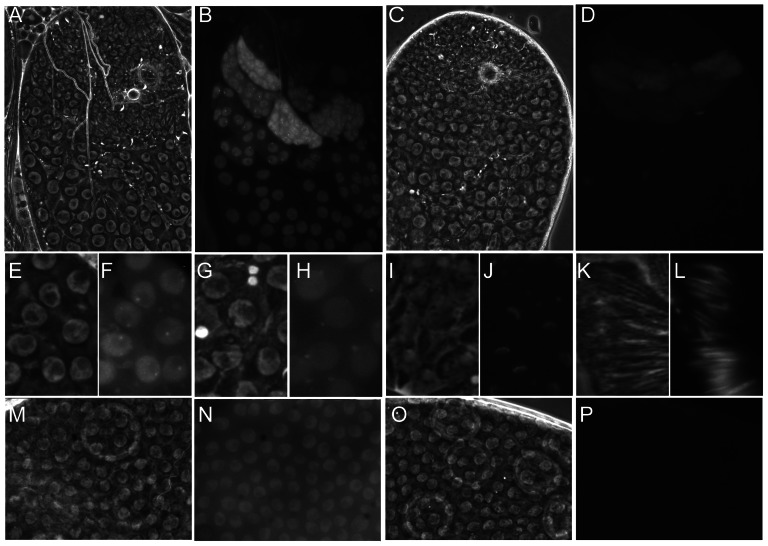
Figure 4. The dynamic localisation of eGFP-Nxt1.
Phase contrast (A, C, E, G, I, K, M, O) and fluorescence images (B, D, F, H, J, L, N, P) of ectopically expressed eGFP-Nxt1(wild type) or eGFP-Nxt1-D126N (D, P). (A–D) Testes tips oriented with younger cells towards the top. When expressed in male germline cells the wild type protein (A, B) localised predominantly to the nucleus, and remained stable as spermatocytes matured. The signal from mutant protein was dramatically weaker, and predominantly cytoplasmic (C, D). In early primary spermatocytes the WT protein localised to an intra-nuclear dot, adjacent to the nucleolus (F) as well as throughout the nucleoplasm. As spermatocytes matured the protein relocated to one or more cytoplasmic puncta, frequently found adjacent to the uniformly labelled nucleus (H). Early elongation spermatids showed cytoplasmic puncta and eGFP-Nxt1 localisation to one face of the nuclear envelope (J). Label persisted until late elongation in spermatid nuclei (L). In the ovarian follicular epithelium the wild type eGFP-tagged protein was predominantly nuclear (N), while the D126N form of the protein was not detected (P).